Quickstart for PDF Extract API (Node.js)
To get started using Adobe PDF Extract API, let's walk through a simple scenario - taking an input PDF document and running PDF Extract API against it. Once the PDF has been extracted, we'll parse the results and report on any major headers in the document. In this guide, we will walk you through the complete process for creating a program that will accomplish this task.
Prerequisites
To complete this guide, you will need:
- Node.js - Node.js version 18.0 or higher is required.
- An Adobe ID. If you do not have one, the credential setup will walk you through creating one.
- A way to edit code. No specific editor is required for this guide.
Step One: Getting credentials
1) To begin, open your browser to https://acrobatservices.adobe.com/dc-integration-creation-app-cdn/main.html?api=pdf-extract-api. If you are not already logged in to Adobe.com, you will need to sign in or create a new user. Using a personal email account is recommend and not a federated ID.
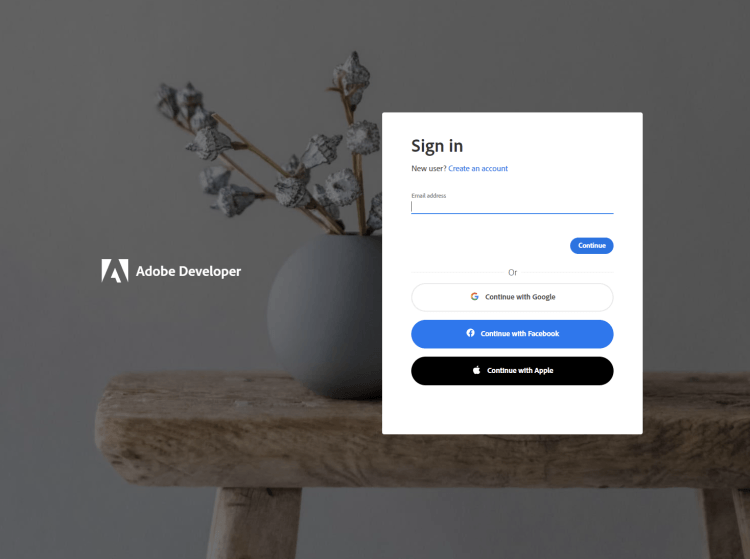
2) After registering or logging in, you will then be asked to name your new credentials. Use the name, "New Project".
3) Change the "Choose language" setting to "Node.js".
4) Also note the checkbox by, "Create personalized code sample." This will include a large set of samples along with your credentials. These can be helpful for learning more later.
5) Click the checkbox saying you agree to the developer terms and then click "Create credentials."
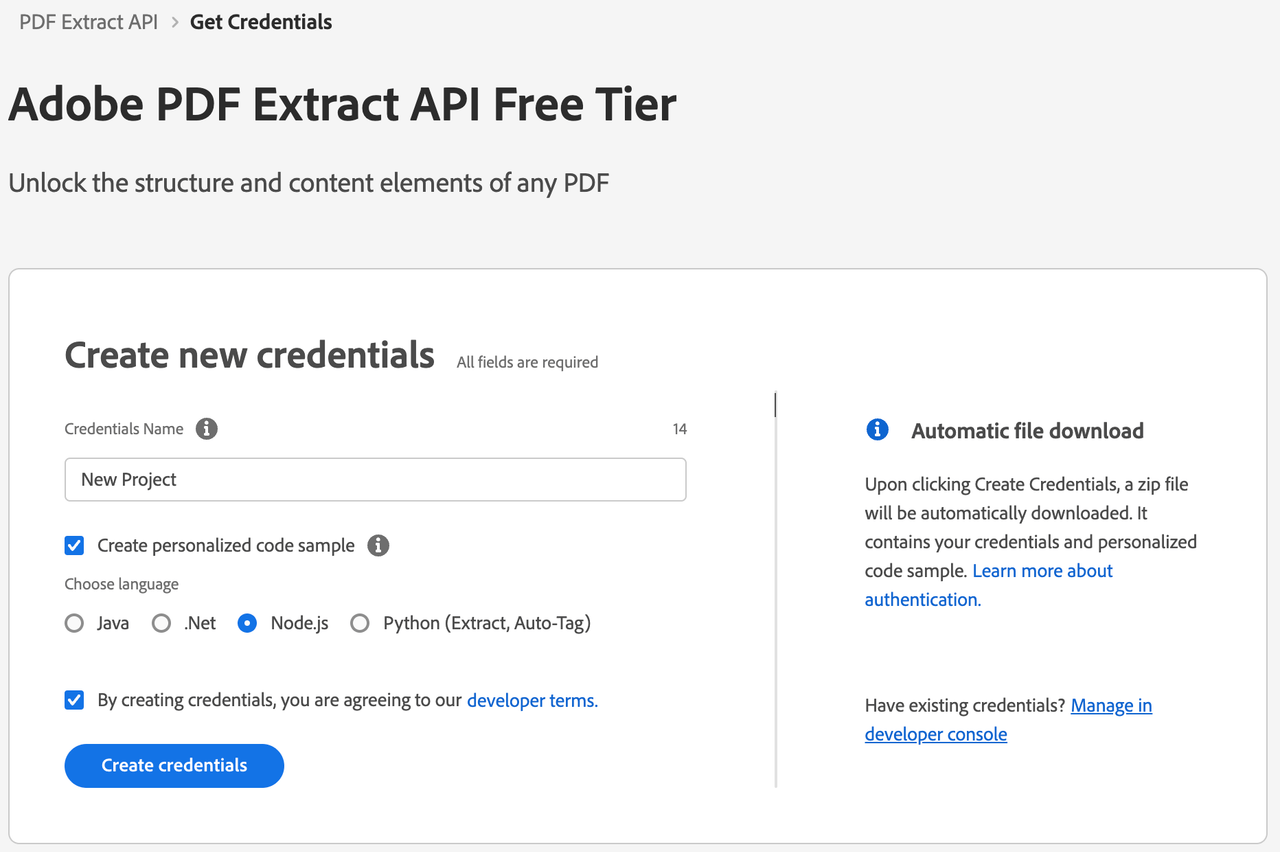
6) After your credentials are created, they are automatically downloaded:
Step Two: Setting up the project
1) In your Downloads folder, find the ZIP file with your credentials: PDFServicesSDK-Node.jsSamples.zip. If you unzip that archive, you will find a folder of samples and the pdfservices-api-credentials.json file.
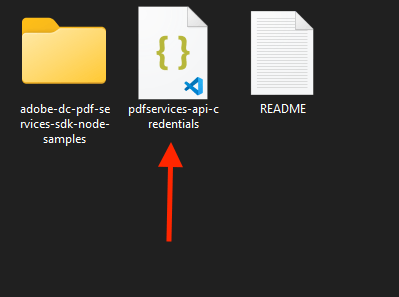
2) Take the pdfservices-api-credentials.json file and place it in a new directory. Remember that these credential files are important and should be stored safely.
3) At the command line, change to the directory you created, and initialize a new Node.js project with npm init -y
4) Install the Adobe PDF Services Node.js SDK by typing npm install --save @adobe/pdfservices-node-sdk at the command line.
5) Install a package to help us work with ZIP files. Type npm install --save adm-zip.
At this point, we've installed the Node.js SDK for Adobe PDF Services API as a dependency for our project and have copied over our credentials files.
Our application will take a PDF, Adobe Extract API Sample.pdf (downloadable from here) and extract it's contents. The results will be saved as a ZIP file, ExtractTextInfoFromPDF.zip. We will then parse the results from the ZIP and print out the text of any H1 headers found in the PDF.
6) In your editor, open the directory where you previously copied the credentials. Create a new file, extract.js.
Now you're ready to begin coding.
Step Three: Creating the application
1) We'll begin by including our required dependencies:
Copied to your clipboardconst {ServicePrincipalCredentials,PDFServices,MimeType,ExtractPDFParams,ExtractElementType,ExtractPDFJob,ExtractPDFResult} = require("@adobe/pdfservices-node-sdk");const fs = require("fs");const AdmZip = require('adm-zip');
2) Set the environment variables PDF_SERVICES_CLIENT_ID and PDF_SERVICES_CLIENT_SECRET by running the following commands and replacing placeholders YOUR CLIENT ID and YOUR CLIENT SECRET with the credentials present in pdfservices-api-credentials.json file:
Windows:
set PDF_SERVICES_CLIENT_ID=<YOUR CLIENT ID>set PDF_SERVICES_CLIENT_SECRET=<YOUR CLIENT SECRET>
MacOS/Linux:
export PDF_SERVICES_CLIENT_ID=<YOUR CLIENT ID>export PDF_SERVICES_CLIENT_SECRET=<YOUR CLIENT SECRET>
3) Next, we setup the SDK to use our credentials.
Copied to your clipboard// Initial setup, create credentials instanceconst credentials = new ServicePrincipalCredentials({clientId: process.env.PDF_SERVICES_CLIENT_ID,clientSecret: process.env.PDF_SERVICES_CLIENT_SECRET});// Creates a PDF Services instanceconst pdfServices = new PDFServices({credentials});
4) Now, let's upload the asset:
Copied to your clipboardconst inputAsset = await pdfServices.upload({readStream,mimeType: MimeType.PDF});
We define what PDF will be extracted. (You can download the source we used here.) In a real application, these values would be typically be dynamic.
5) Now, let's create the parameters and the job:
Copied to your clipboard// Create parameters for the jobconst params = new ExtractPDFParams({elementsToExtract: [ExtractElementType.TEXT]});// Creates a new job instanceconst job = new ExtractPDFJob({inputAsset, params});
This set of code defines what we're doing (an Extract operation), it defines parameters for the Extract job. PDF Extract API has a few different options, but in this example, we're simply asking for the most basic of extractions, the textual content of the document.
6) The next code block submits the job and gets the job result:
Copied to your clipboard// Submit the job and get the job resultconst pollingURL = await pdfServices.submit({job});const pdfServicesResponse = await pdfServices.getJobResult({pollingURL,resultType: ExtractPDFResult});// Get content from the resulting asset(s)const resultAsset = pdfServicesResponse.result.resource;const streamAsset = await pdfServices.getContent({asset: resultAsset});
This code runs the Extraction process, gets the content of the result zip in stream asset.
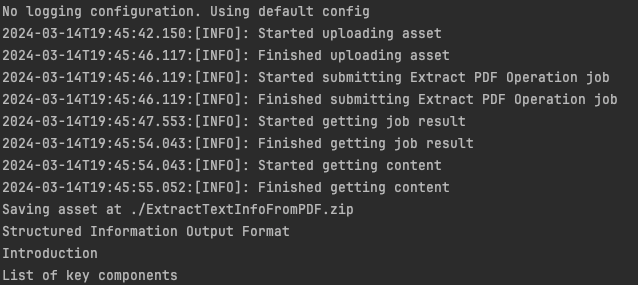
7) The next code block saves the result at the specified location:
Copied to your clipboard// Creates a write stream and copy stream asset's content to itconst outputFilePath = "./ExtractTextInfoFromPDF.zip";console.log(`Saving asset at ${outputFilePath}`);const writeStream = fs.createWriteStream(outputFilePath);streamAsset.readStream.pipe(writeStream);
Here's the complete application (extract.js):
8) In this block, we read in the ZIP file, extract the JSON result file, and parse it:
Copied to your clipboardlet zip = new AdmZip(outputFilePath);let jsondata = zip.readAsText('structuredData.json');let data = JSON.parse(jsondata);
9) Finally, we can loop over the result and print out any found element that is an H1:
Copied to your clipboarddata.elements.forEach(element => {if(element.Path.endsWith('/H1')) {console.log(element.Text);}});
Here's the complete application (extract.js):
Copied to your clipboardconst {ServicePrincipalCredentials,PDFServices,MimeType,ExtractPDFParams,ExtractElementType,ExtractPDFJob,ExtractPDFResult} = require("@adobe/pdfservices-node-sdk");const fs = require("fs");const AdmZip = require('adm-zip');(async () => {let readStream;try {// Initial setup, create credentials instanceconst credentials = new ServicePrincipalCredentials({clientId: process.env.PDF_SERVICES_CLIENT_ID,clientSecret: process.env.PDF_SERVICES_CLIENT_SECRET});// Creates a PDF Services instanceconst pdfServices = new PDFServices({credentials});// Creates an asset(s) from source file(s) and uploadreadStream = fs.createReadStream("./Adobe Extract API Sample.pdf");const inputAsset = await pdfServices.upload({readStream,mimeType: MimeType.PDF});// Create parameters for the jobconst params = new ExtractPDFParams({elementsToExtract: [ExtractElementType.TEXT]});// Creates a new job instanceconst job = new ExtractPDFJob({inputAsset, params});// Submit the job and get the job resultconst pollingURL = await pdfServices.submit({job});const pdfServicesResponse = await pdfServices.getJobResult({pollingURL,resultType: ExtractPDFResult});// Get content from the resulting asset(s)const resultAsset = pdfServicesResponse.result.resource;const streamAsset = await pdfServices.getContent({asset: resultAsset});// Creates a write stream and copy stream asset's content to itconst outputFilePath = "./ExtractTextInfoFromPDF.zip";console.log(`Saving asset at ${outputFilePath}`);const writeStream = fs.createWriteStream(outputFilePath);streamAsset.readStream.pipe(writeStream);let zip = new AdmZip(outputFilePath);let jsondata = zip.readAsText('structuredData.json');let data = JSON.parse(jsondata);data.elements.forEach(element => {if(element.Path.endsWith('/H1')) {console.log(element.Text);}});} catch (err) {console.log("Exception encountered while executing operation", err);} finally {readStream?.destroy();}})();
Next Steps
Now that you've successfully performed your first operation, review the documentation for many other examples and reach out on our forums with any questions. Also remember the samples you downloaded while creating your credentials also have many demos.


