UI Customization
The Embed API provides a number of options for customizing the user interface and user interactions with the PDF. Features which are enabled by default can be explicitly disabled. Optional configurations include controls for:
- Enabling and disabling commenting, form filling, and other user interactions (applicable only in Full Window embed mode).
- Enabling and disabling PDF download and print options.
- Modifying the PDF display to Fit Page or Fit Width (applicable in Full Window and Lightbox embed modes).
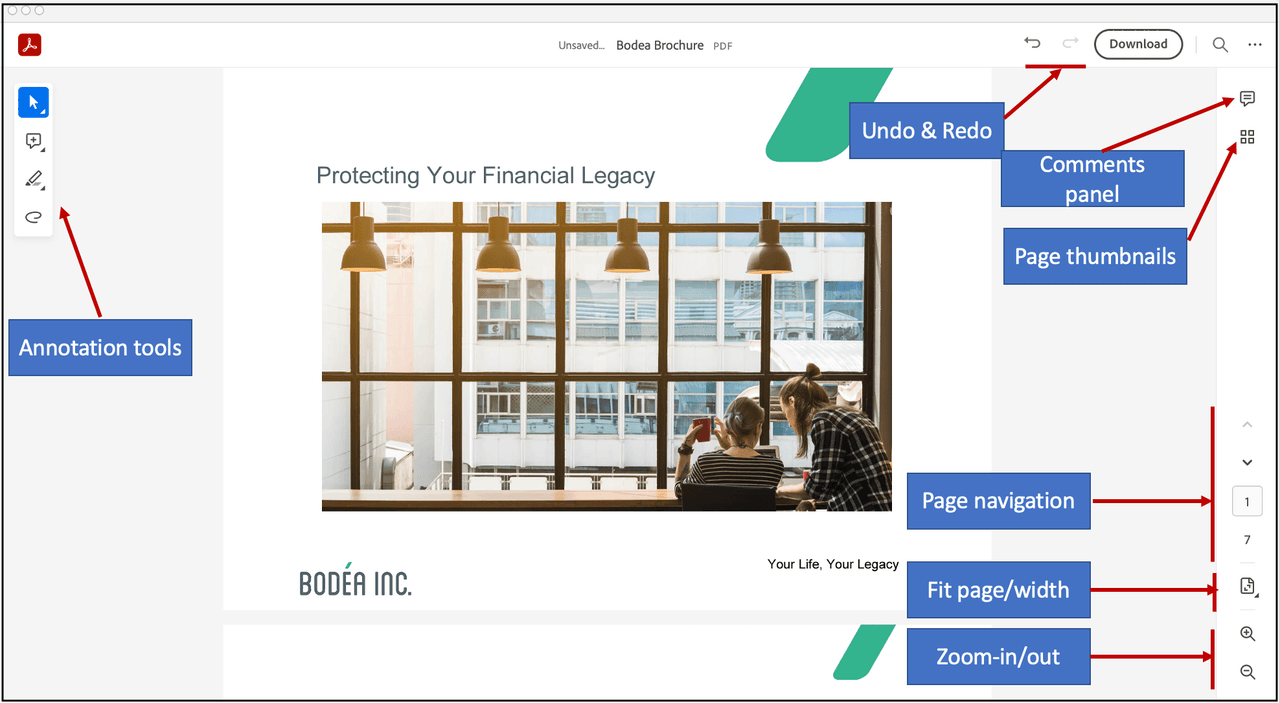
Menu and tool options
You can control various options provided by PDF Embed API and customize the PDF viewer as per your requirements.
Initialize the AdobeDC.View object with your client ID and
then invoke the previewFile API on AdobeDC.View object.
The previewFile API reads the variable values and toggles
features on and off accordingly.
In the example below, the embed mode is set as FULL_WINDOW and the download PDF option is disabled from the
overflow menu in the top bar in full window embed mode with showDownloadPDF set to false. The
PDF zoom control options are disabled with showZoomControl set to false.
Example
Copied to your clipboard<div id="adobe-dc-view"></div><script src="https://acrobatservices.adobe.com/view-sdk/viewer.js"></script><script type="text/javascript">// Store the UI options in a constantconst previewConfig = {embedMode: "FULL_WINDOW",showDownloadPDF: false,showZoomControl: false}document.addEventListener("adobe_dc_view_sdk.ready", function () {var adobeDCView = new AdobeDC.View({clientId: "<YOUR_CLIENT_ID>", divId: "adobe-dc-view"});// Consume previewConfig here. . .adobeDCView.previewFile({content:{location: {url: "https://acrobatservices.adobe.com/view-sdk-demo/PDFs/Bodea Brochure.pdf"}},metaData:{fileName: "Bodea Brochure.pdf"}}, previewConfig);});</script>
Configuration options for AdobeDC.View object
This table lists down the various configurations which can be passed while initializing the AdobeDC.View object.
| Variable | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
clientId | None | You'll need a client ID to use the Adobe PDF Embed API. To get one, click HERE. |
divId | "adobe-dc-view" | The div ID where your PDF will render. |
locale | "en-US" | You can select another language by passing the locale code variable. For more details, see the section Language support. |
reportSuiteId | None | Pass the report suite ID to collect PDF analytics in Adobe Analytics. For more details, see the section Adobe analytics. |
measurementId | None | Pass the measurement ID to collect PDF analytics in Google Analytics. For more details, see the section Google Analytics. |
sendAutoPDFAnalytics | true | Use this configuration to disable PDF analytics collection in Adobe Analytics or Google Analytics. For more details, see the section Control analytics collection. |
Configuration options for previewFile API
This table lists down the various preview configurations which can be passed to the previewFile API to customize the PDF viewer.
| Variable | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
showZoomControl | true | Set this to false to hide the zoom-in and zoom-out options available in the right-hand panel. This configuration will work for full window and lightbox embed modes. |
showAnnotationTools | true | If true, tools such as add text, sticky note, highlight, and so on appear in the quick tools menu on the left-hand side in full window embed mode. For more details, see Comments and Markup. |
showFullScreen | true | By default, the full screen toggle appears in the bottom toolbar in sized container embed mode. Set this to false to hide the full screen toggle. |
defaultViewMode | "" | This variable takes a string value of "FIT_WIDTH", "FIT_PAGE", "TWO_COLUMN" or "TWO_COLUMN_FIT_PAGE". 1. FIT_WIDTH: Expands the page horizontally to the full width of the document pane. 2. FIT_PAGE: Displays the entire page in the current view pane. 3. TWO_COLUMN: Displays two pages of the PDF side by side in the current view pane. 4. TWO_COLUMN_FIT_PAGE: Displays two pages of the PDF side by side where the entire two pages are displayed in the current view pane. Note that end users can also toggle the view mode via the Fit Width, Fit Page or Two-Column button on the right-hand panel. In addition to these, there are two other view modes which are supported only in mobile browsers: 1. CONTINUOUS: This mode displays all the document pages one after the other and users can easily navigate through the pages by scrolling up or down. 2. SINGLE_PAGE: This mode displays only a single document page at a time and doesn’t show any adjoining page. Users can use the swipe gesture to navigate to other pages which will be displayed one at a time. |
enableFormFilling | true | If true, form filling is enabled and users can edit fields in full window embed mode. |
showDownloadPDF | true | If true, PDF can be downloaded in all embed modes. Set this to false to disable PDF download. |
showPrintPDF | true | If true, PDF can be printed in all embed modes. Set this to false to disable PDF printing. |
exitPDFViewerType | "CLOSE" | The top bar in lightbox embed mode contains the close button by default to close the PDF preview which can be configured to Back button by setting exitPDFViewerType to "RETURN". |
showThumbnails | true | Page thumbnails are available by default in full window and lightbox embed modes. Set this to false if you want to hide the thumbnails from the right-hand panel. |
showBookmarks | true | PDF bookmarks are available by default in full window and lightbox embed modes. Set this to false if you want to hide the bookmarks from the right-hand panel. |
enableLinearization | false | Set this to true to enable PDF linearization. For more details, see the section PDF linearization. |
enableAnnotationAPIs | false | Set this to true to add, update and delete PDF annotations programmatically in full window embed mode. For more details, see the section Annotations API overview. |
includePDFAnnotations | false | This configuration is used with enableAnnotationAPIs to access existing PDF annotations. For more details, see the section Annotations API overview. |
enableSearchAPIs | false | Set this to true to perform search operation in the PDF programmatically. For more details, see the section Search APIs. |
showDisabledSaveButton | false | Set this to true to show the save button in disabled state even when there are no changes to be saved to the PDF. |
focusOnRendering | Varies according to embed mode | With this configuration, website developers have the flexibility to control if the PDF should take focus when it is rendered. For more details, see the section Focus on PDF rendering. |
showFullScreenViewButton | true | Set this to false to hide the full-screen option available in the right-hand panel. This configuration will work for full window and lightbox embed modes. |
Annotations
For details, see Comments and Markup.
Callbacks & workflows
The PDF Embed API supports workflow customization via callbacks. By registering callbacks with specified parameters, website developers can control workflows related to saving files, user profiles, user settings, and so on.
Every callback requires the following three parameters:
- Callback type: One of SAVE_API, STATUS_API, GET_USER_PROFILE, GET_USER_SETTING_API, or SET_USER_SETTING_API
- Function: A JavaScript function which returns a promise.
- Options: Additional options passed to the callback to control its behaviour in certain scenarios.
You can only register one callback per type; for example, you can register one callback for save and one for status.
AdobeDC.View exposes registerCallback, so the code looks something
like:
Copied to your clipboardadobeDCView.registerCallback(<Callback Type>,<Function>,options);
The second parameter is a function which returns a promise which either resolves or fails with a response object consisting of code and data. This promise should resolve in the case of successful execution, and it should be rejected in the case of an error. Pass the relevant code along with the promises:
Copied to your clipboardreturn new Promise((resolve, reject) => {/* Successresolve({code: AdobeDC.View.Enum.ApiResponseCode.SUCCESS,data: {...}}); *//* Failurereject({code: AdobeDC.View.Enum.ApiResponseCode.FAIL,data: {...}}); */}
User Profiles
The user profile callback allows the user to specify user profile details such as first name, last name, and email address. By default, if you do not register a user profile callback, the user name is displayed as "Guest" in the comments panel.
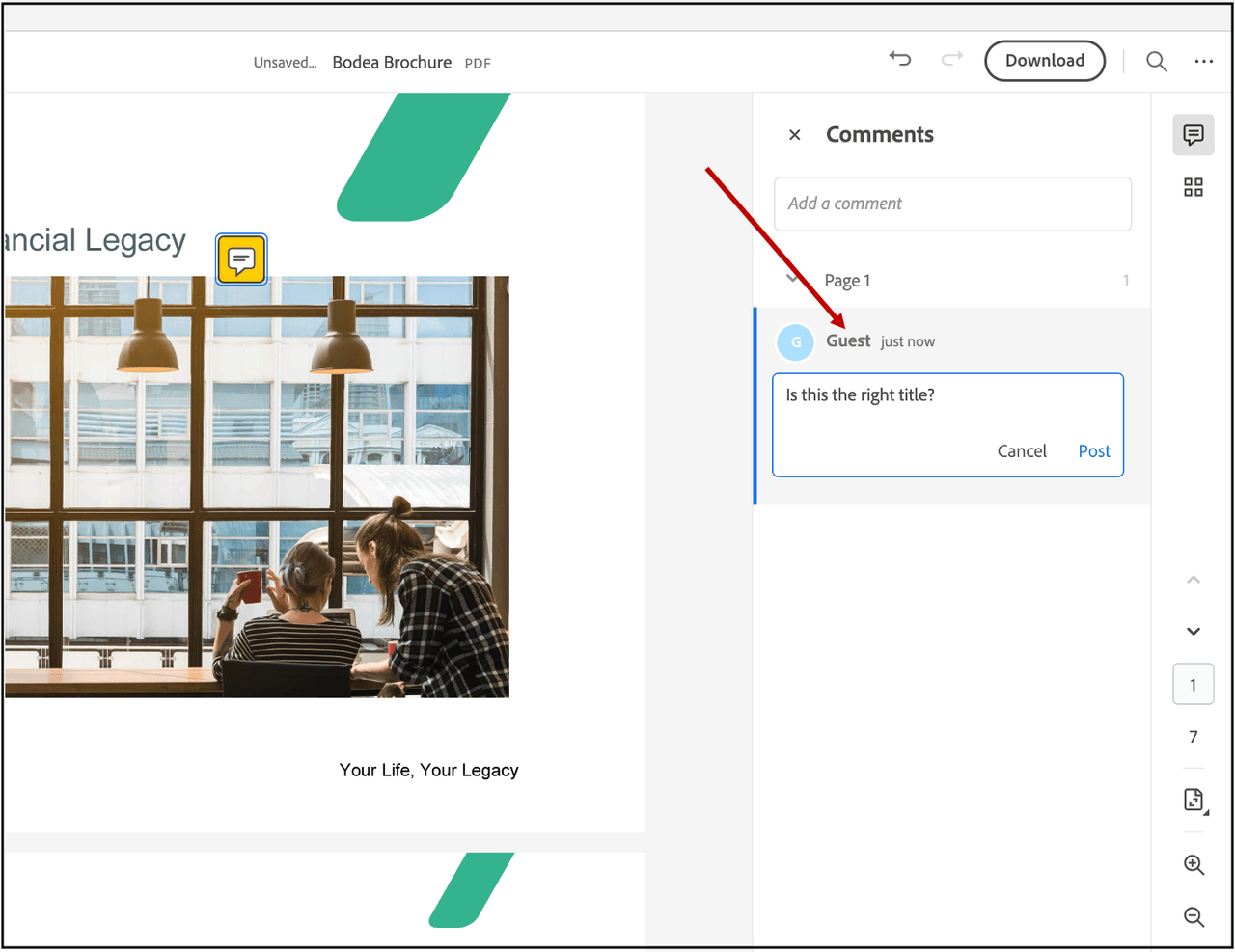
When the callback is registered, user annotations are associated with the corresponding username.
User profile callback signature
Copied to your clipboardconst profile = {userProfile: {name: <name of user>,firstName: <first name>,lastName: <last name>,email: <user email>}};adobeDCView.registerCallback(AdobeDC.View.Enum.CallbackType.GET_USER_PROFILE_API,function() {return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {resolve({code: AdobeDC.View.Enum.ApiResponseCode.SUCCESS,data: profile});});},{});
User settings
Users can update the color of an annotation by clicking on the PDF annotation and changing the color from the toolbar. The updated color is applied to all new annotations of that type added to the PDF. Also, when any annotation tool is selected for the first time, there is a coach mark displayed to educate users about the annotation tool which goes away after a few seconds.
Previously, the default implementation of these user preferences was that the browser used to remember the updated annotation color and also whether the coach mark for a selected annotation tool has been displayed or not. This was achieved by storing this data in the local storage of the PDF Embed API domain. This is now deprecated and PDF Embed API does not store this data.
By default, these preferences are lost when the PDF reloads. As a result, the updated annotation color is not remembered (default annotation color will be applied in this case) and users will see annotation tool coach marks again when the PDF reloads.
Website developers can improve this experience by registering the user setting callbacks. There are two callbacks involved:
- SET_USER_SETTING_API: This callback saves user-specific settings.
- GET_USER_SETTING_API: This callback fetches the current user setting.
Developers can provide their own implementation using these callbacks and save the user preferences wherever they like.
User settings callback signature
Copied to your clipboardadobeDCView.registerCallback(AdobeDC.View.Enum.CallbackType.SET_USER_SETTING_API,function(setting) {/* Add your custom implementation here to save the user setting */......return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {resolve({code: AdobeDC.View.Enum.ApiResponseCode.SUCCESS});});},{});adobeDCView.registerCallback(AdobeDC.View.Enum.CallbackType.GET_USER_SETTING_API,function() {/* Fetch the user setting */return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {resolve({code: AdobeDC.View.Enum.ApiResponseCode.SUCCESS,data: {setting: <USER_STORED_SETTING>}});});},{});
Find the working code sample
here under
/More Samples/Save User Preferences/. In this code sample, the user
setting callbacks are used to save the user preferences in the local
storage of the website domain. Using this implementation, the browser
remembers the updated annotation color and also shows the coach mark
only once for every annotation tool in the current browser.
This is only an example and it is up to the website developer how they do the actual implementation of saving the user preferences.
Save a PDF
The Save button on the top bar is not visible unless the PDF is
modified: it only becomes active after PDF modification (there are
changes to actually save). For example, when showAnnotationTools is
true, users can add an annotation or comment, and you can provide them
with the option to save the modified PDF to a local or networked
location.
A user cannot add comments or edit PDF files that are secure, protected, or read-only. The annotation tools as well as the save button are hidden for such files.
Note that while the Save button is hidden by default, you can show the
button even when there are no changes to save by setting
showDisabledSaveButton to true and passing it as a preview
configuration to the previewFile API. In this case, the save button
appears in disabled state until the PDF is modified.
Copied to your clipboard{showDisabledSaveButton: <Boolean, default=false>,}
Save callback
This callback allows users to save the updated PDF buffer which can then be stored in an external file storage system.
- If you do not register a callback: When any annotation is added to the PDF, a download button appears in the top bar. Click on the download button to save the updated PDF to the user’s local machine. The default location is often the Downloads folder.
- If you do register a callback: When any annotation is added to the PDF, a save button appears in the top bar. Your code can enable saving the modified document to an external file storage system like OneDrive or Google Drive. In this case, the code varies with the website developer’s implementation.
Users can trigger the save functionality by either clicking on the Save or Download button manually or by pressing Ctrl+S on the keyboard. You should register the callback to receive the modified file content when the user initiates the save.
To control the save callback behavior, you can pass the following options:
autoSaveFrequency: Optional. Default value is 0. The save callback supports auto-saving so that manual saving is not required. The value is the time in seconds after which the PDF is auto-saved if there are any unsaved changes and no other annotation changes are made in the meantime. Using this configuration, the document is saved even if the user does not manually save. You must set this parameter to a numeric value greater than 0.enableFocusPolling: Optional. Default value is false. When true, a PDF with unsaved changes is auto-saved whenever the user focus shifts from the current PDF preview (for example, by opening a new tab in the same browser). When false, auto-save does not happen. Set this parameter to true if you want this to work.showSaveButton: Optional. Default value is true. Set this to false if you don't want the save button to be displayed at all, not even when the PDF is modified. When set to false, the save button is never displayed and save operation will be done through auto-save or through the keyboard by pressing Ctrl+S.
The second callback parameter is a JavaScript function returning a Promise which either resolves or fails with a response object containing code and data. The function parameters include:
metaData: Information about the filecontent: The ArrayBuffer of file contentoptions: (optional) Additional user options passed to the function to control its behavior in certain cases. For instance, thesaveAsoption is passed here when the current user saves a copy of a changed PDF when multiple users are modifying the same file (See the FILE_MODIFIED case below).
Save callback signature
Copied to your clipboardconst saveOptions = {autoSaveFrequency: <Number, default=0>,enableFocusPolling: <Boolean, default=false>,showSaveButton: <Boolean, default=true>}adobeDCView.registerCallback(AdobeDC.View.Enum.CallbackType.SAVE_API,function(metaData, content, options) {/* Add your custom save implementation here...and based on that resolve or reject response in given format */return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {resolve({code: AdobeDC.View.Enum.ApiResponseCode.SUCCESS,data: {/* Updated file metadata after successful save operation */metaData: <File MetaData>}});});},saveOptions);
The website developer can write their own save implementation in this function and should send the response object with the appropriate code and data in the following format:
- SUCCESS: Use this response code to denote a successful save operation where the response data contains the updated file metadata.
- FAIL: Use the FAIL response code when the save API fails. Response data is optional in this case. The user will see an error popup and should retry saving.

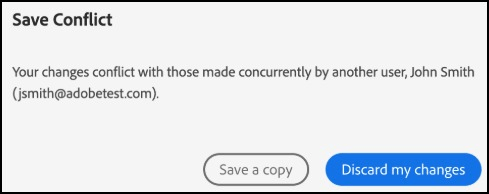
- FILE_MODIFIED: Use the response code FILE_MODIFIED to capture the case when two users simultaneously modify a single PDF. This case only occurs for shared files. The save functionality will fail for the current user if the file content has been previously modified by another user. The response data will contain the name and email of the other user modifying the same file.
In this scenario, the current user sees a popup with two options:
- Save a copy: Choosing the Save a copy button initiates the
save callback again and saves a copy of the PDF with the current
user’s changes. The
{saveAs: true}option is passed to theoptionsparameter of the function to denote that a new PDF is saved. - Discard my changes: Discards the current user’s changes and reloads the PDF.
Save callback
Copied to your clipboard/* Options to control save behavior */const saveOptions = {autoSaveFrequency: <Number, default=0>,enableFocusPolling: <Boolean, default=false>,showSaveButton: <Boolean, default=true>}/* Register save callback */adobeDCView.registerCallback(AdobeDC.View.Enum.CallbackType.SAVE_API,function(metaData, content, options) {/* Write down your own save implementation here... and based on that resolve or reject response in given format *//* Save callback success case */return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {resolve({code: AdobeDC.View.Enum.ApiResponseCode.SUCCESS,data: {metaData: Object.assign(metaData, {fileName: <UPDATED_FILE_NAME>})}});});/* Save callback failure case *//* return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {reject({code: AdobeDC.View.Enum.ApiResponseCode.FAIL,data: {<Optional>}});}); *//* Save callback file modified case *//* return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {resolve({code: AdobeDC.View.Enum.ApiResponseCode.FILE_MODIFIED,data: {modifiedBy: {name: <Username of the user who modified the file>,mail: <Email of the user who modified the file>,}}});}); */},saveOptions);
Status callback
The status callback allows you to poll the status of the file to check
whether the currently open file is changed by another user or not. This
file status polling occurs after a fixed interval of time defined in the
filePollFrequency option. Use both the save and status callbacks
together to achieve the complete save experience including auto-save and
file status polling.
While you can specify additional options to control the status
callback, both autoSaveFrequency and enableFocusPolling are
deprecated for the status callback. Developers are advised to use
these options with the save callback.
filePollFrequency: Optional. Default value is 10 seconds. The time in seconds after which the file is polled for changes. To disable file status polling, setfilePollFrequencyto 0. By default, file status polling starts when there are unsaved changes made in the PDF by the current user.keepPolling: Optional. Default value is false (boolean). SetkeepPollingto true if you want file status polling to work continuously even if there are no unsaved changes made to the file by the current user. The frequency of the file status polling is governed by the time specified infilePollFrequency.
Status callback signature
Copied to your clipboardconst statusOptions = {filePollFrequency: <Number, default=10>,keepPolling: <Boolean, default=false>};adobeDCView.registerCallback(AdobeDC.View.Enum.CallbackType.STATUS_API,function(metaData) {/* Resolve or reject response in given format */return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {resolve({code: AdobeDC.View.Enum.ApiResponseCode.SUCCESS,data: {<Optional>}});});},statusOptions);
The second parameter of the callback is a JavaScript function returning
a Promise which either resolves or fails with a response object
containing a code and data. metaData is the only function parameter,
and it refers to the file information. The response code in the Promise
can take either SUCCESS or FILE_MODIFIED:
SUCCESS: Use the response code SUCCESS to denote successful file polling and that the file has no changes made by another user. Response data is optional here.
FILE_MODIFIED: Use the response code FILE_MODIFIED to capture the case of conflicting updates made by another user in a file sharing scenario. Response data will contain the name and email of the other user modifying the same file. Note the following:
- If the Promise returns FILE_MODIFIED when the current user has not changed the file, that denotes that the file was already modified by another user and the current user is viewing an old version of the file. The user sees a popup with the "Get Latest Version" option which will reload the latest version of the file.

- If the Promise returns FILE_MODIFIED after the current user has changed the file, that denotes that two users are modifying the same file simultaneously. In this scenario, the current user sees a popup with two options: Save a copy saves a copy of the PDF with the current user’s changes while Discard my changes discards the current user’s changes and reloads the PDF.
Status callback
Copied to your clipboardconst statusOptions = {filePollFrequency: <Number, default=10>,keepPolling: <Boolean, default=false>};adobeDCView.registerCallback(AdobeDC.View.Enum.CallbackType.STATUS_API,function(metaData) {/* Resolve or reject response in given format *//* Status callback success case */return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {resolve({code: AdobeDC.View.Enum.ApiResponseCode.SUCCESS,});});/* Status callback file modified case *//* return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {resolve({code: AdobeDC.View.Enum.ApiResponseCode.FILE_MODIFIED,data: {modifiedBy: {name: <Username of the user who modified the file>,mail: <Email of the user who modified the file>,}}});}); */},statusOptions);
Viewer API
The PDF Embed API provides a number of viewer APIs for customizing the user interface and user interactions with the PDF. These APIs can be used to perform UI customizations programmatically at run-time.
GetAPIs Interface
The getAPIs interface allows you to invoke any of the viewer APIs as follows:
Copied to your clipboard<html><head><title>Adobe Acrobat Services PDF Embed API Sample</title><meta charset="utf-8"/><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge,chrome=1"/><meta id="viewport" name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"/></head><body style="margin: 0px"><div id="adobe-dc-view"></div><script src="https://acrobatservices.adobe.com/view-sdk/viewer.js"></script><script type="text/javascript">document.addEventListener("adobe_dc_view_sdk.ready", function(){var adobeDCView = new AdobeDC.View({clientId: "<YOUR_CLIENT_ID>", divId: "adobe-dc-view"});var previewFilePromise = adobeDCView.previewFile({content: {location: {url: "https://acrobatservices.adobe.com/view-sdk-demo/PDFs/Bodea Brochure.pdf"}},metaData: {fileName: "Bodea Brochure.pdf"}});previewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {// All viewer APIs can be invoked here});});});</script></body></html>
Zoom APIs
These APIs can be used to perform zoom operations on the PDF programmatically. These APIs are supported in all embed modes except in-line embed mode.
getZoomLimits
This API returns the minimum and maximum allowed zoom levels of the PDF.
Input parameters
N/A
API output
Returns a Promise which,
- Resolves with a JSON object including the minimum and maximum zoom level of the PDF.
{ minZoom: <MIN_ZOOM_LEVEL>, maxZoom: <MAX_ZOOM_LEVEL> } - Rejects with an error object that includes a code and message.
API signature
Copied to your clipboardpreviewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.getZoomAPIs().getZoomLimits().then(result => console.log(result)).catch(error => console.log(error));});});
zoomIn
This API zooms in on the PDF and magnifies the PDF view to the next zoom level. The magnified zoom level will never exceed the maximum zoom level of the PDF.
Input parameters
N/A
API output
Returns a Promise which,
- Resolves with the updated zoom level.
- Rejects with an error object that includes a code and message.
API signature
Copied to your clipboardpreviewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.getZoomAPIs().zoomOut().then(result => console.log(result)).catch(error => console.log(error));});});
zoomOut
This API zooms out of the PDF and reduces the PDF view to the previous zoom level. The reduced zoom level will never be less than the minimum zoom level of the PDF.
Input parameters
N/A
API output
Returns a Promise which,
- Resolves with the updated zoom level.
- Rejects with an error object that includes a code and message.
API signature
Copied to your clipboardpreviewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.getZoomAPIs().zoomOut().then(result => console.log(result)).catch(error => console.log(error));});});
setZoomLevel
This API accepts a float value as input and sets the zoom level of the PDF to that value. The input must lie between the minimum and maximum allowed zoom levels of the PDF.
If the input passed is less than the minimum zoom level, then the minimum zoom level is applied to the PDF. Similarly, if the input passed is greater than the maximum zoom level, then the maximum zoom level is applied.
Input parameters
<ZOOM_LEVEL: Float>
API output
Returns a Promise which,
- Resolves with the updated zoom level.
- Rejects with an error object that includes a code and message.
API signature
Copied to your clipboardpreviewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.getZoomAPIs().setZoomLevel(<ZOOM_LEVEL>).then(result => console.log(result)).catch(error => console.log(error));});});
Search APIs
This API can be used to search for a term in the PDF programmatically. This API is supported in all embed modes.
In order to enable search APIs, the configuration variable
enableSearchAPIs should be set to true and passed as a preview
configuration to the previewFile API.
Copied to your clipboard<html><head><title>Adobe Acrobat Services PDF Embed API Sample</title><meta charset="utf-8"/><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge,chrome=1"/><meta id="viewport" name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"/></head><body style="margin: 0px"><div id="adobe-dc-view"></div><script src="https://acrobatservices.adobe.com/view-sdk/viewer.js"></script><script type="text/javascript">document.addEventListener("adobe_dc_view_sdk.ready", function(){var adobeDCView = new AdobeDC.View({clientId: "<YOUR_CLIENT_ID>", divId: "adobe-dc-view"});var previewFilePromise = adobeDCView.previewFile({content: {location: {url: "https://acrobatservices.adobe.com/view-sdk-demo/PDFs/Bodea Brochure.pdf"}},metaData: {fileName: "Bodea Brochure.pdf"}}, { enableSearchAPIs: true });previewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {// All viewer APIs can be invoked here});});});</script></body></html>
The document search option is not available in UI when search APIs are enabled.
The search API takes a search term of String value as input and searches for that term in the entire document. The first occurrence of the search term is highlighted in the PDF, starting from the current page in view.
Input parameters
<SEARCH_STRING: String>
API output
Returns a Promise which,
- Resolves with a JSON object containing the following interfaces:
onResultsUpdate()next()previous()clear()
- Rejects with an error object that includes a code and message.
API signature
Copied to your clipboardpreviewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.search(<SEARCH_STRING>).then(searchObject => console.log(searchObject)).catch(error => console.log(error));});});
onResultsUpdate
Users can register a callback function and pass as an input to the
onResultsUpdate() function. This callback function will be triggered
every time a search operation takes place through the search API and the
search result is highlighted in the PDF. The callback function will
receive important information about the current search result in the
form of a JSON. The JSON will include information such as current page
number, current search result index, total number of search results and
status.
Copied to your clipboard{currentResult: {pageNumber: Integer, // Current page number in viewindex: Integer, // Index of the current highlighted search result},totalResults: Integer, // Total number of search results found till the time callback function is executedstatus: String // Status of search result till the time callback function is executed. Values can be "IN_PROGRESS" or "COMPLETED".}
Input parameters
N/A
API output
Returns a Promise which,
- Resolves to true on successful operation. When operation is successful, the callback function is executed and receives information about the search results in the form of a JSON. Resolves to false when
onResultsUpdate()operation fails. - Rejects with an error object that includes a code and message.
API signature
Copied to your clipboardfunction callbackFunction(searchResult) {console.log("Current search result: ", searchResult);}previewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.search(<SEARCH_STRING>).then(searchObject => {searchObject.onResultsUpdate(callbackFunction).then(result => console.log(result)).catch(error => console.log(error));}).catch(error => console.log(error));});});
next
This function will highlight and navigate to the next search result in the PDF.
Input parameters
N/A
API output
Returns a Promise which,
- Resolves to true on successful operation and the next search result is highlighted in the PDF. Resolves to false when
next()operation fails. - Rejects with an error object that includes a code and message.
API signature
Copied to your clipboardpreviewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.search(<SEARCH_STRING>).then(searchObject => {searchObject.next().then(result => console.log(result)).catch(error => console.log(error));}).catch(error => console.log(error));});});
previous
This function will highlight and navigate to the previous search result in the PDF.
Input parameters
N/A
API output
Returns a Promise which,
- Resolves to true on successful operation and the previous search result is highlighted in the PDF. Resolves to false when
previous()operation fails. - Rejects with an error object that includes a code and message.
API signature
Copied to your clipboardpreviewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.search(<SEARCH_STRING>).then(searchObject => {searchObject.previous().then(result => console.log(result)).catch(error => console.log(error));}).catch(error => console.log(error));});});
clear
This function will cancel the ongoing search operation and clear the search results.
Input parameters
N/A
API output
Returns a Promise which,
- Resolves to true on successful operation. Stops ongoing search operation and clears the search results. Resolves to false when
clear()operation fails. - Rejects with an error object that includes a code and message.
API signature
Copied to your clipboardpreviewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.search(<SEARCH_STRING>).then(searchObject => {searchObject.clear().then(result => console.log(result)).catch(error => console.log(error));}).catch(error => console.log(error));});});
Find the working code sample for search and zoom APIs
here under
/More Samples/Viewer APIs/Search and Zoom APIs
Bookmark APIs
These APIs programmatically access existing PDF bookmarks. Note that only the Full Window embed mode supports these APIs.
getBookmarks
This API returns the list of existing PDF bookmarks Each bookmark item in this list is represented as a JSON containing important information such as ID, title and the list of nested bookmarks residing under this bookmark.
Copied to your clipboard{id: Number // Unique identifier of the bookmarktitle: String, // Title of the bookmarkchildren: [ CHILD_BOOKMARK_1, CHILD_BOOKMARK_2, ... ] // List of nested bookmarks which exists under this bookmark}
Input parameters
N/A
API output
Returns a Promise which,
- Resolves with the list of bookmarks available in the PDF.
[ Bookmark_1, Bookmark_2, ...] - Rejects with an error object that includes a code and message.
API signature
Copied to your clipboardpreviewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.getBookmarkAPIs().getBookmarks().then(result => console.log(result)).catch(error => console.log(error));});});
openBookmark
This API accepts a bookmark ID as input and navigates to that particular PDF bookmark.
Input parameters
<BOOKMARK_ID>
API output
Returns a Promise which,
- Resolves to true on successful API execution and the user navigates to that particular bookmark. Resolves to false when the bookmark does not exist in the PDF.
- Rejects with an error object that includes a code and message.
API signature
Copied to your clipboardconst bookmark_ID = <BOOKMARK_ID>;previewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.getBookmarkAPIs().openBookmark(bookmark_ID).then(result => console.log(result)).catch(error => console.log(error));});});
Find the working code sample
here under
/More Samples/Viewer APIs/Bookmark APIs
Attachment APIs
These APIs access the existing attachments in the PDF programmatically.
getAttachments
This API returns the list of existing attachments in the PDF. Each attachment item in this list is represented as a JSON containing important information such as name, mime type, description, creation date and modified date.
Copied to your clipboard{name: String // Name of the attachment filedescription: String, // Description of the attachmentmimeType: String // Mime type of the attachment filecreated: Date // Date when the attachment was createdmodified: Date // Date when the attachment was modified}
Input parameters
N/A
API output
Returns a Promise which,
- Resolves with the list of attachments available in the PDF:
[ Attachment_1, Attachment_2,...] - Every attachment item in this list will contain information such as
name,description,mimeType,createdandmodified. - Rejects with an error object that includes a code and message.
API signature
Copied to your clipboardpreviewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.getAttachmentAPIs().getAttachments().then(result => console.log(result)).catch(error => console.log(error));});});
getAttachmentBuffer
This API accepts the name of an attachment as input and returns the ArrayBuffer of the attachment content.
Input parameters
<ATTACHMENT_NAME: String>
API output
Returns a Promise which,
- Resolves with the ArrayBuffer of the attachment file:
{ buffer: Int8Array } - Rejects with an error object that includes a code and message.
API signature
Copied to your clipboardpreviewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.getAttachmentAPIs().getAttachmentBuffer(<ATTACHMENT_NAME>).then(result => console.log(result)).catch(error => console.log(error));});});
Find the working code sample
here under
/More Samples/Viewer APIs/Attachment APIs
getPDFMetadata
This API returns basic information about the PDF fetched from the PDF dictionary; for example, the PDF's number of pages and title.
Input parameters
N/A
API output
Returns a Promise which,
- Resolves with a JSON object which includes the number of pages and title of PDF if successful:
{ numPages: <NUMBER_OF_PAGES>, pdfTitle: <PDF_TITLE> } - Rejects with an error object that includes a code and message.
API signature
Copied to your clipboardpreviewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.getPDFMetadata().then(result => console.log(result)).catch(error => console.log(error));});});
getXMPMetadata
XMP (Extensible Metadata Platform) is a technology developed by Adobe which provides a common XML framework to store metadata in digital documents. XMP Metadata includes information about the document and its contents, such as the author's name, keywords, and copyright information.
getXMPMetadata checks the PDF for XMP metadata and returns it if
present. The API accepts two optional input parameters.
- The first optional input parameter takes a list of XMP metadata fields. The API returns the values of only these fields. If no field is passed, then it returns the default field values.
- The second optional input parameter takes a boolean value. If true, the API will also return the complete XMP metadata stream. The default value is false.
Input parameters
(fields = [<field1>, <field2>, ...], includeRawStream = <Boolean>)
API output
Returns a Promise which,
- Resolves with the JSON object containing the XMP metadata and XML stream (if
includeRawStreamis set to true) if successful:{ xmpMetadata: <XMP_METADATA>, xmpStream: <XML> } - Rejects with an error object that includes a code and message.
API signature
Copied to your clipboardconst fields = ["dc:title", "dc:creator", "xmp:CreateDate"];const includeRawStream = true;previewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.getXMPMetadata(fields, includeRawStream).then(result => console.log(result)).catch(error => console.log(error));});});
getSelectedContent
If a user selects any content in the viewer, then the selected content can be fetched using this API. This API currently only works with text selection.
Input parameters
N/A
API output
Returns a Promise which,
- Resolves with a JSON object including the type of content and actual selected content if successful:
{ type: "<CONTENT_TYPE>", data: "<SELECTED_CONTENT>" } - Rejects with an error object that includes a code and message.
API signature
Copied to your clipboardpreviewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.getSelectedContent().then(result => console.log(result)).catch(error => console.log(error));});});
setCursor
This API sets the page cursor to any cursor style, such as help, wait, crosshair, etc.
Input parameters
A string denoting the cursor style: <Cursor_Type>
API output
N/A
API signature
Copied to your clipboardconst cursor_type = <Cursor_Type>;previewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.setCursor(cursor_type).then(() => console.log("Success")).catch(error => console.log(error));});});
resetCursor
This API revokes an applied cursor style and reverts it to the default cursor style.
Input parameters
N/A
API output
N/A
API signature
Copied to your clipboardpreviewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.resetCursor();});});
getCurrentPage
This API returns the current page number of the in focus page.
Input parameters
N/A
API output
Returns a Promise which,
- Resolves with the current page number if successful
- Rejects with an error object that includes a code and message.
API signature
Copied to your clipboardpreviewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.getCurrentPage().then(result => console.log(result)).catch(error => console.log(error));});});
getPageZoom
This API takes the PDF page number as input and returns the zoom level of that page.
Input parameters
<Page_Number>
API output
Returns a Promise which,
- Resolves with the zoom level if successful
- Rejects with an error object that includes a code and message.
API signature
Copied to your clipboardpreviewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.getPageZoom(<Page_Number>).then(result => console.log(result)).catch(error => console.log(error));});});
gotoLocation
This API enables navigation to any PDF page. It accepts a page number as input. You can also pass the x and y coordinates on the page as optional input parameters to enable navigation to a particular location on the page. When no coordinates are passed, the default coordinates are (0, 0).
Navigation will not work if the specified page number exceeds the PDF page limit. Moreover, the x and y input coordinates must be within the PDF page width and height limit. If either the x or y coordinate is not within the page limit, then they default to 0.
Input parameters
(<Page_Number>, <X_Coordinate>, <Y_Coordinate>)
API output
Returns a Promise which,
- Resolves if successful
- Rejects with an error object that includes a code and message.
API signature
Copied to your clipboardpreviewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.gotoLocation(<Page_Number>, <X_Coordinate>, <Y_Coordinate>).then(() => console.log("Success")).catch(error => console.log(error));});});
clearPageSelection
This API accepts a page number as input and clears any text selection applied to the page.
Input parameters
<Page_Number>
API output
Returns a Promise which,
- Resolves if successful
- Rejects with an error object that includes a code and message.
API signature
Copied to your clipboardpreviewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.clearPageSelection(pageNumber).then(() => console.log("Success")).catch(error => console.log(error));});});
enableTextSelection
This API controls text selection in PDF. The default is enabled (true). Note that disabling text selection also disables the highlight annotation tool from the quick tools menu on the left-hand side.
Input parameters
Boolean
API output
Returns a Promise which,
- Resolves if successful
- Rejects with an error object that includes a code and message.
API signature
Copied to your clipboardconst allowTextSelection = false;previewFilePromise.then(adobeViewer => {adobeViewer.getAPIs().then(apis => {apis.enableTextSelection(allowTextSelection).then(() => console.log("Success")).catch(error => console.log(error));});});


