Browse View
AEM Assets View offers the ability to customize the ActionBar, QuickActions and HeaderMenu in the Browse View.
UI Extensibility is supported in Assets Ultimate only.
To get access to Assets View UI extensibility, create and submit an Adobe Customer Support case. You can provide documentation feedback by clicking "Log an issue".
The Browse View in the AEM Assets View refers to the asset listing pages such as Assets, Collections, Recent, Search and Trash.
Definitions
ActionBar is the blue bar with actions that appears at the top when one or more assets in the Browse View are selected.

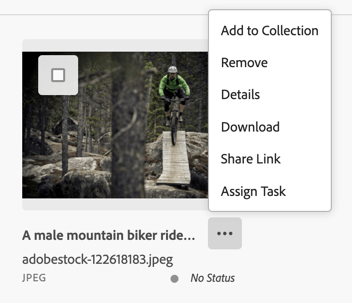
QuickActions is the dropdown menu from the More action button (shown as ⋯) next to each asset.
HeaderMenu is the set of buttons at the top right of the browse screen. Custom buttons may be added between the ellipses menu and default HeaderMenu buttons.
Extensions should use the aem/assets/browse/1 extension point to utilize extensibility services of the Browse View.
An extension needs to implement both actionBar and quickActions namespace to be recognized by Assets View. Extensions may optionally implement the headerMenu namespace.
Custom ActionBar actions and QuickActions menu actions
This extensibility feature allows context-aware customization of the ActionBar actions and the QuickActions menu actions associated with the selected assets.
Using the actionBar namespace, custom actions could be added to the ActionBar after the list of built-in actions, and
the built-in actions could be overridden or hidden based on the context and the selected assets.
In this example, a custom action is added to the ActionBar after the list of built-in ActionBar actions.
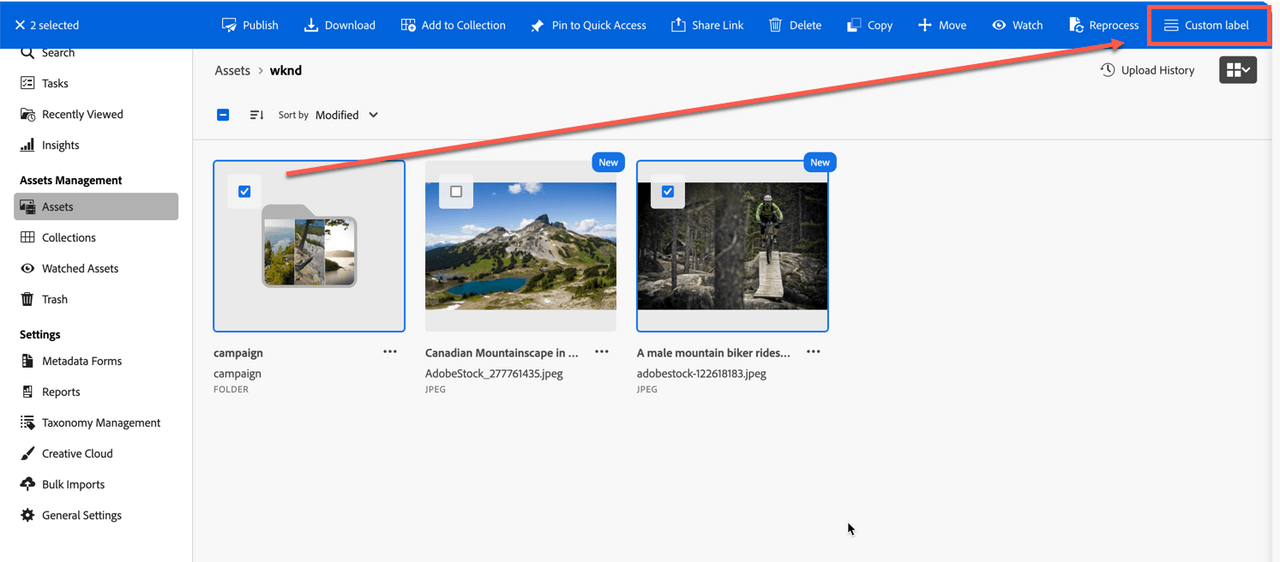
Using the quickActions namespace, built-in QuickActions menu actions can be overridden or hidden based on the context and the
selected asset.
Custom HeaderMenu buttons
This extensibility feature allows context-aware customization of the HeaderMenu buttons.
Using the headerMenu namespace, custom buttons could be added to the HeaderMenu before the list of built-in buttons based on the context.
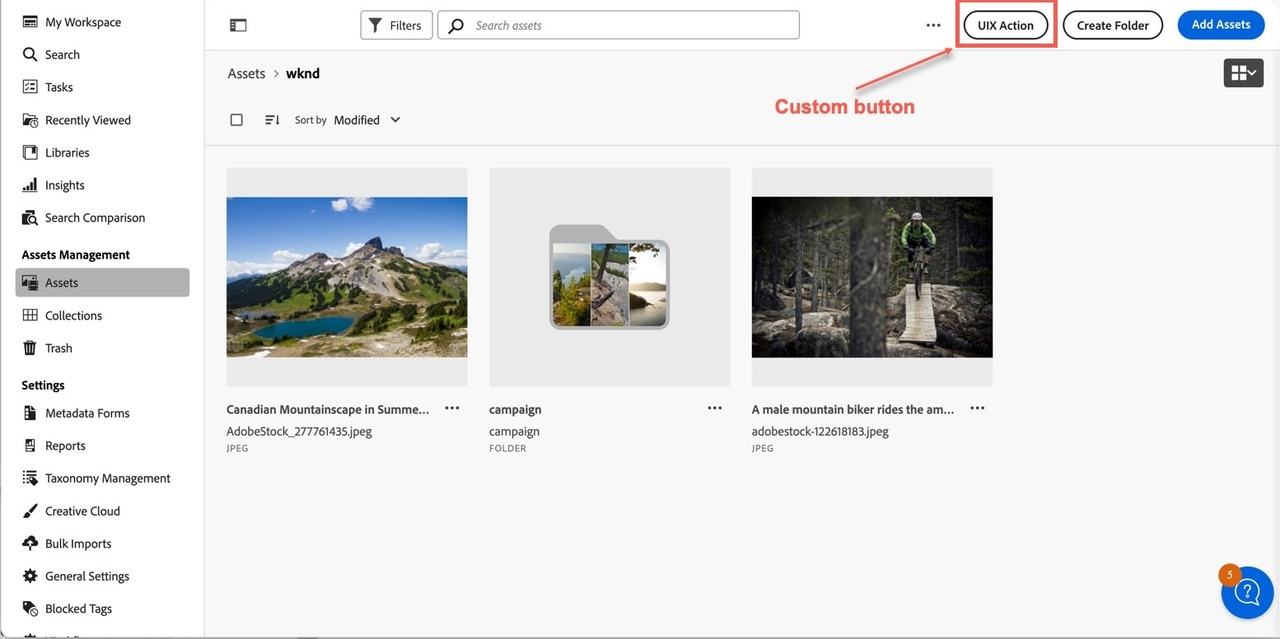
In this example, a custom button is added to the HeaderMenu before the list of built-in HeaderMenu buttons.
API Reference
This API reference section is further broken down into two parts: the API provided by the AEM Assets View host application to the extension and the API provided by the extension to the AEM Assets View host application.
Host API Reference
In addition to the Common API provided by AEM Assets View to all extensions,
the host application provides the following definitions that are specific to the aem/assets/browse/1 extension point: actionBar, quickActions and headerMenu namespaces.
Browsing context
Assets View supports assets browsing experiences in multiple modes, or "contexts". The current context is communicated to Extension APIs, so that the custom code within Extension can adapt to the state of Assets View.
The supported browsing contexts are:
| Browsing Context | Description |
|---|---|
assets | Main asset browsing experience |
collections | Collections listing |
recent | Recent listing |
search | Search results listing |
trash | Assets in trash |
Built-in actions
The host application allows hiding certain built-in actions. Depending on the browsing content, below is the list of action ids of actions that can be hidden:
| Browsing Context | Action IDs that can be hidden or overridden |
|---|---|
assets | "edit", "openInExpress", "reprocess", "copy", "move", "rename", "bulkRename", "managePermissions", "delete", "publish", "download", "share" |
collections | "openInExpress", "rename", "managePermissions", "delete", "download", "share" |
recent | - |
search | "edit", "openInExpress", "reprocess", "copy", "move", "rename", "bulkRename", "managePermissions", "delete", "publish", "download", "share" |
trash | "delete" |
Extension API Reference
The extension definition object passed by the extension to the register() function defines the actionBar, quickActions and headerMenu namespaces.
The methods in these namespaces provide the capabilities to
- Add custom actions to the ActionBar
- Hide or customize built-in actions in the ActionBar and QuickActions
- Add custom buttons to the HeaderMenu
actionBar namespace
The actionBar namespace includes these 3 methods
getActions({ context, resourceSelection })getHiddenBuiltInActions({ context, resourceSelection })overrideBuiltInAction({ actionId, context, resourceSelection })
actionBar.getActions({ context, resourceSelection })
Description: returns an array of custom action descriptors or an empty array if no custom actions should be added to the ActionBar in the specified context for the selected assets.
Parameters:
- context (
string): current browsing context. - resourceSelection (
object): an object representing the asset selection.- resources (
array): an array of selected assets.- id (
string): selected asset URN. - path (
string): selected asset path.
- id (
- resources (
Returns (array) an array of custom action descriptors or an empty array if no custom actions should be added to the ActionBar.
Each array element is a custom action descriptor that is a JSON with the following properties:
id(string): action id, unique within given extension.label(string): Custom action title.icon(string): Name of the React-Spectrum workflow icon.onClick(function): An activation handler.
Example:
Copied to your clipboardactionBar: {getActions: ({ context, resourceSelection }) => {return [{'id': 'customId','icon': 'Form','label': 'Custom label','onClick': async () => {// ...}}];},}
getHiddenBuiltInActions({ context, resourceSelection })
Description: returns an array of built-in action id that should be hidden in the specified context for the selected assets.
This method is called by the host application to determine which built-in actions are to be hidden. The host calls this method once whenever the asset selection changes.
Extension code should ensure that this method returns fast because the host application blocks the rendering of the ActionBar until the actions' visibility could be determined. In particular it is recommended not to use backend server calls in this method.
Parameters:
- context (
string): current browsing context - resourceSelection (
object): an object representing the asset selection- resources (
array): an array of selected assets.- id (
string): selected asset URN. - path (
string): selected asset path.
- id (
- resources (
Returns (array) an array of action ids that should be hidden from the ActionBar, or an empty array in case no action needs to be hidden
Example:
Copied to your clipboardgetHiddenBuiltInActions: ({ context, resourceSelection }) => {return [];},
overrideBuiltInAction({ actionId, context, resourceSelection })
Description: Return true to indicate the Host should perform the built-in action, false otherwise.
This method is called by the Host when the user activates one of the built-in actions, before invoking the actual action handler. The method returns true if the Extension had performed custom action processing and the Host should not invoke built-in action handler. Otherwise the method call returns false, to indicate that the Extension had ignored the invocation and the Host should use built-in action handler.
Parameters:
- actionId (
string): built-in action id. - context (
string): current browsing context. - resourceSelection (
object): an object representing the asset selection.- resources (
array): an array of selected assets.- id (
string): selected asset URN. - path (
string): selected asset path.
- id (
- resources (
Returns (boolean) false for Host to use built-in action handler, true to skip built-in handler and stop
Example:
Copied to your clipboardoverrideBuiltInAction: ({ actionId, context, resourceSelection }) => {//do some custom tasksreturn true; // skip the Host's built-in handler and stop},
quickActions namespace
The quickActions namespace include these 2 methods
getHiddenBuiltInActions({ context, resource })overrideBuiltInAction({ actionId, context, resource })
getHiddenBuiltInActions({ context, resource })
Description: returns an array of built-in action id that should be hidden in the specified context for the selected asset.
This method is called by the host application to determine which built-in actions are to be hidden. The host calls this method once whenever QuickAction menu is triggered.
Extension code should ensure that this method returns fast because the host application blocks the rendering of the QuickActions until the actions' visibility could be determined. In particular it is recommended not to use backend server calls in this method.
Parameters:
- context (
string): current browsing context. - resource (
object): an object representing the selected asset.- id (
string): selected asset URN. - path (
string): selected asset path.
- id (
Returns (array) an array of action ids that should be hidden from the QuickActions menu, or an empty array in case no action needs to be hidden.
Example:
Copied to your clipboardgetHiddenBuiltInActions: ({ context, resource }) => {return [];},
overrideBuiltInAction: ({ actionId, context, resource })
Description:
This method is called by the Host when the user activates one of the built-in actions, before invoking the actual action handler. The method returns true if the Extension had performed custom action processing and the Host should not invoke built-in action handler. Otherwise the method call returns false, to indicate that the Extension had ignored the invocation and the Host should use built-in action handler.
Parameters:
- actionId (
string): built-in action id. - context (
string): current browsing context. - resource (
object): an object representing the selected asset.- id (
string): selected asset URN. - path (
string): selected asset path.
- id (
Returns (boolean) false for Host to use built-in action handler, true to skip built-in handler and stop.
Example:
Copied to your clipboardoverrideBuiltInAction: ({ actionId, context, resource }) => {//do some custom tasksreturn true;},
headerMenu namespace
The headerMenu namespace currently has the following method
getButtons({context, resource})
getButtons({context, resource})
Description: Returns an array of custom header button definitions that will be added to the application's header menu. These buttons are rendered alongside built-in header buttons and provide a way for extensions to add custom functionality accessible from the top header area on browse screens.
Parameters:
- context (
string): current browsing context. - resource (
object): Information about the current location being browsed- id (
string): The unique identifier of the current location - path (
string): The path of the current location - In contexts that do not support a notion of active resource, like
'trash','search'or'recent', theresourceargument will beundefined. For'assets'and'collections'context, theresourceis a JSON object withidandpath, even for the root folder.
- id (
Returns: (array) - An array of button configuration objects, where each object contains:
- id (
string): Unique identifier for the button within the extension - label (
string): Display text for the button - icon (
string): Name of the React-Spectrum workflow icon - onClick (
function): Callback function executed when button is clicked, receives{context, resource}as parameter - variant (
string, optional): Button visual style, defaults to'primary'- Supported values:
'accent','primary','secondary','negative'
- Supported values:
Example:
Copied to your clipboard// Extension implementationconst headerMenuAPI = {async getButtons({ context, resource }) {// Only show buttons in assets contextif (context !== 'assets') {return [];}// adds 2 custom buttons to the application header menureturn [{id: 'export-metadata',label: 'Export Metadata',icon: 'Download', // React Spectrum Workflow icon namevariant: 'secondary',onClick: async ({ context, resource }) => {console.log('Exporting metadata for:', resource);// Custom export logic here}},{id: 'custom-workflow',label: 'Start Workflow',icon: 'Workflow',onClick: async ({ context, resource }) => {// Custom workflow logic here}}];}};
Examples
These code snippets demonstrate how to add a custom action to the ActionBar, add buttons to the HeaderMenu, hide built-in actions or override the built-in action handlers from the ActionBar and QuickActions menu in the Browse View. (The examples below serve illustrative purposes thus omit certain import statements and other non-important parts.)
The ExtensionRegistration component initializes the extension registration process by calling the register() function
provided by the @adobe/uix-guest library.
The objects passed to the register() function describe the extension and its capabilities. In particular, it declares
that the extension uses the actionBar, quickActions and headerMenu namespaces and declares required methods for these namespaces.
This example demonstrates the minimal set of namespaces and methods required for a browse extension to be recognized by the Host application.
Copied to your clipboardfunction ExtensionRegistration() {const init = async () => {const guestConnection = await register({id: extensionId,methods: {actionBar: {async getActions({ context, resourceSelection }) {return [];},async getHiddenBuiltInActions({ context, resourceSelection }) {return [];},async overrideBuiltInAction({ actionId, context, resourceSelection }) {return false;},},quickActions: {async getHiddenBuiltInActions({ context, resource }) {return [];},async overrideBuiltInAction({ actionId, context, resource }) {return false;},},headerMenu: {async getButtons ({ context, resource }) {return []},},},});};init().catch(console.error);return <Text>IFrame for integration with Host (AEM Assets View)...</Text>;}export default ExtensionRegistration;
Example of adding custom actions
Here is an example for adding a custom action after the built-in actions in the ActionBar.
In the example below, the context and the number of selected assets are considered for the decision of adding a custom
action labeled with Custom label along with the Form icon is added in the assets context when the number of
selected assets is 1.
Copied to your clipboardfunction ExtensionRegistration() {const init = async () => {const guestConnection = await register({id: extensionId,methods: {actionBar: {async getActions({ context, resourceSelection }) {if (context === 'assets' && resourceSelection.resources.length === 1) {return [{'id': 'customId','icon': 'Form','label': 'Custom label','onClick': async () => {// ...}}];}return [];},// ...},quickActions: {// ...},// ...},});};init().catch(console.error);return <Text>IFrame for integration with Host (AEM Assets View)...</Text>;}export default ExtensionRegistration;
Example of hiding built-in actions
Here are the examples for hiding built-in actions from the ActionBar and the QuickActions menu.
In this example, the Delete action is hidden from the ActionBar only in the trash context. It does not hide any
actions in the other contexts.
Copied to your clipboardfunction ExtensionRegistration() {const init = async () => {const guestConnection = await register({id: extensionId,methods: {actionBar: {// ...async getHiddenBuiltInActions({ context, resourceSelection }) {if (context === 'trash') {return ['delete'];}return [];},},quickActions: {// ...},},});};init().catch(console.error);return <Text>IFrame for integration with Host (AEM Assets View)...</Text>;}
In the example below, the Delete action is hidden from the QuickActions menu only in the trash context. It does not
hide any actions in the other contexts.
Copied to your clipboardfunction ExtensionRegistration() {const init = async () => {const guestConnection = await register({id: extensionId,methods: {actionBar: {// ...},quickActions: {async getHiddenBuiltInActions({ context, resource }) {if (context === 'trash') {return ['delete'];}return [];},},// ...},});};init().catch(console.error);return <Text>IFrame for integration with Host (AEM Assets View)...</Text>;}
Example of overriding built-in actions
Here are the examples for overriding the built-in actions from the ActionBar and the QuickActions menu.
In this example, the Download action is overridden in the ActionBar in any applicable context. The extension will
determine if the user has permission to download the asset selection. If the user does not have sufficient permision,
a dialog will be displayed and the built-in handler in the Host application will be skipped.
The built-in handlers will be executed when the user has sufficient permission to download as well as for other built-in actions.
Copied to your clipboardfunction ExtensionRegistration() {const init = async () => {const guestConnection = await register({id: extensionId,methods: {actionBar: {// ...async overrideBuiltInAction({ actionId, context, resourceSelection }) {if (actionId === 'download') {// determines the user's permission to downloadconst canDownload = ...// shows an info dialog explaining why the user cannot download and return true to skip built-in handler and stopif (!canDownload) {guestConnection.host.modal.openDialog({title: 'Download',contentUrl: '/#modal-download-warning',type: 'modal',size: 'S',payload: { /* arbitrary payload */ }});// skip built-in handlerreturn true;}}// continue to execute built-in handlerreturn false;},},quickActions: {// ...},},});};init().catch(console.error);return <Text>IFrame for integration with Host (AEM Assets View)...</Text>;}
Example of user interaction with overriding built-in actions
In this example, the Modal API is used to let the user confirm or cancel a default action based on their selection. The extension presents a confirmation dialog and waits for the user's response. If the user confirms, the built-in handler is executed by returning false. If the user cancels, the built-in handler is skipped by returning true.
Copied to your clipboardactionBar: {async overrideBuiltInAction({ actionId, context, resourceSelection: { resources } }) {const { promise, resolve } = Promise.withResolvers();guestConnection.host.modal.openDialog({title: `Confirm ${actionId}`,contentUrl: '#confirm',type: 'S',payload: {callback: resolve}});return await promise;},}
In the example below, the Download action is overridden in the QuickActions menu in any applicable context. The extension will
determine if the user has permission to download the asset selection. If the user does not have sufficient permision,
a dialog will be displayed and the built-in handler in the Host application will be skipped.
The built-in handlers will be executed when the user has sufficient permission to download as well as for other built-in actions.
Copied to your clipboardfunction ExtensionRegistration() {const init = async () => {const guestConnection = await register({id: extensionId,methods: {quickActions: {// ...async overrideBuiltInAction({ actionId, context, resource }) {if (actionId === 'download') {// determines the user's permission to downloadconst canDownload = ...// shows an info dialog explaining why the user cannot download and return true to skip built-in handler and stopif (!canDownload) {guestConnection.host.modal.openDialog({title: 'Download',contentUrl: '/#modal-download-warning',type: 'modal',size: 'S',payload: { /* arbitrary payload */ }});// skip built-in handlerreturn true;}}// continue to execute built-in handlerreturn false;},},actionBar: {// ...},},});};init().catch(console.error);return <Text>IFrame for integration with Host (AEM Assets View)...</Text>;}
To open a custom dialog from custom ActionBar actions, QuickActions menu actions or HeaderMenu, refer to the Modal API provided by AEM Assets View to all extensions for implementation of dialog management.


