Configuring a Secure Proxy
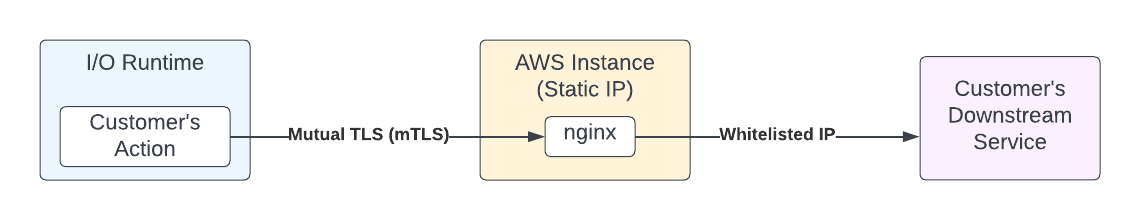
Runtime does not expose egress IPs due to security reasons. If a customer needs a way to secure the communication with their downstream services using IP whitelisting, they can use a proxy in between their backend service and I/O Runtime.
This can be done by the addition of a proxy component (in this example, an AWS EC2 instance running nginx). The proxy component will have a fixed IP address, therefore enabling the use of an IP allowlist to secure your backend service. The communication between I/O Runtime and the proxy component will be secured via mutual TLS (mTLS) communication.
The following steps outline how to:
- Configure the NGINX proxy component to support mutual TLS (mTLS)
- Configure an AppBuilder action to use mTLS to securely communicate with the proxy component
Prerequisite: An EC2 instance with NGINX installed. The official NGINX documentation has more information.
Verify SSH connectivity to the EC2 instance. (screenshot of terminal/template cmd)
Copied to your clipboardssh -i <your-key.pem> ec2-user@<EC2-IPAddress>Generate certificates needed for mTLS (link out to example-mtls project for generating secrets)
- Generate mtls_server.key/.crtCopied to your clipboardopenssl req -x509 -nodes -days 3650 -newkey rsa:4096 -keyout mtls_server.key -out mtls_server.crt
- Generate mtls_client.key/.crtCopied to your clipboardopenssl req -x509 -nodes -days 3650 -newkey rsa:4096 -keyout mtls_client.key -out mtls_client.crt
- Generate mtls_server.key/.crt
Use the referenced file
mtls.conf.exampleand replaceDESTINATION_HOSTwith the final destination you would like to proxy to. For example, if your target host isapi.myhost.comyou would search for the following lineCopied to your clipboardproxy_pass https://DESTINATION_HOSTand replace it such that it looks like
Copied to your clipboardproxy_pass https://api.myhost.comSave the resulting file locally as
mtls.conf(in the same folder as your certificates).Copy sample NGINX configuration to EC2 instance with updated placeholder details. (terminal screenshots for
scpcmds)- First copy files to home folderCopied to your clipboardscp -i <your-key.pem> mtls_server.key mtls_server.crt mtls_client.key mtls_client.crt mtls.conf ec2-user@<EC2-IPAddress>:~/
- Then move them into place (while connected via SSH to the ec2 instance)Copied to your clipboardsudo mv ~/mtls* /etc/nginx/conf.d/
- First copy files to home folder
Restart
nginxVerify you can connect via curl locally from the ec2 instance
Copied to your clipboard$ curl -ki --cert /etc/nginx/conf.d/mtls_client.crt --key /etc/nginx/conf.d/mtls_client.key https://localhost/- (Optional) Create an AMI from your running AWS instance in order to preserve your changes.
In your AppBuilder app, you will need to make changes to wire the mTLS client key and certificate
.env: Add the following lines with paths to your mtls client certificate files.Copied to your clipboard## Support mTLS__AIO_MTLS_CERT=(cat /path/to/mtls_client.crt)__AIO_MTLS_KEY=(cat /path/to/mtls_client.key)app.config.yaml: Add the following default parameters pointing to the environment variables.Copied to your clipboardinputs:__AIO_MTLS_CERT: $__AIO_MTLS_CERT__AIO_MTLS_KEY: $__AIO_MTLS_KEY
In your action code, you can reference these environment variables when making an HTTP request to the proxy component (replace the
PROXY_ENDPOINTwith your AWS EC2 hostname/IP)Copied to your clipboard// configure the client side of mTLSconst options = {cert: params.__AIO_MTLS_CERT,key: params.__AIO_MTLS_KEY,rejectUnauthorized: false, // in test, if you're working with self-signed certificateskeepAlive: false, // switch to true if you're making a lot of calls from this client};const sslConfiguredAgent = new https.Agent(options);try {// Replace the `PROXY_ENDPOINT` with your AWS EC2 hostname/IPconst url = "https://PROXY_ENDPOINT/path/to/resource?param=value"console.log(`Making call to: [${url}]`);// make the request just as you would normally ...const response = await fetch(url, {agent: sslConfiguredAgent, // ... but add the agent we initialised});const responseBody = await response.text();// handle the response as you would see fitconsole.log(responseBody);return { statusCode: 200, body: { resp: responseBody }};} catch (error) {// return the errorconsole.log(error);return { statusCode: 418, body: { error: error }};}Deploy your application to I/O Runtime via
aio app deployand test out the setup by invoking your action.
