Resize and Rescale Elements
Adobe Express offers robust APIs for resizing and rescaling elements, ensuring different behaviors for aspect ratios and visual styling. It's essential to understand the difference between resizing and rescaling to achieve the desired visual results.
Resize vs. Rescale
Resizing adjusts the bounding box of an element while trying to preserve the existing size of visual detailing such as strokes, corners, and fonts.
Rescaling visually scales the entire content larger or smaller, which changes the size of visual styling elements such as stroke width, corner detailing, and font size proportionally.
IMPORTANT: These APIs are currently experimental only and should not be used in any add-ons you will be distributing until they have been declared stable. To use them, you will first need to set the experimentalApis flag to true in the requirements section of the manifest.json.
Rescale Elements Proportionally
Rescaling operations maintain the aspect ratio of elements while changing their overall size. The visual styling elements (strokes, fonts, etc.) scale proportionally with the content.
Example: Rescale by Width
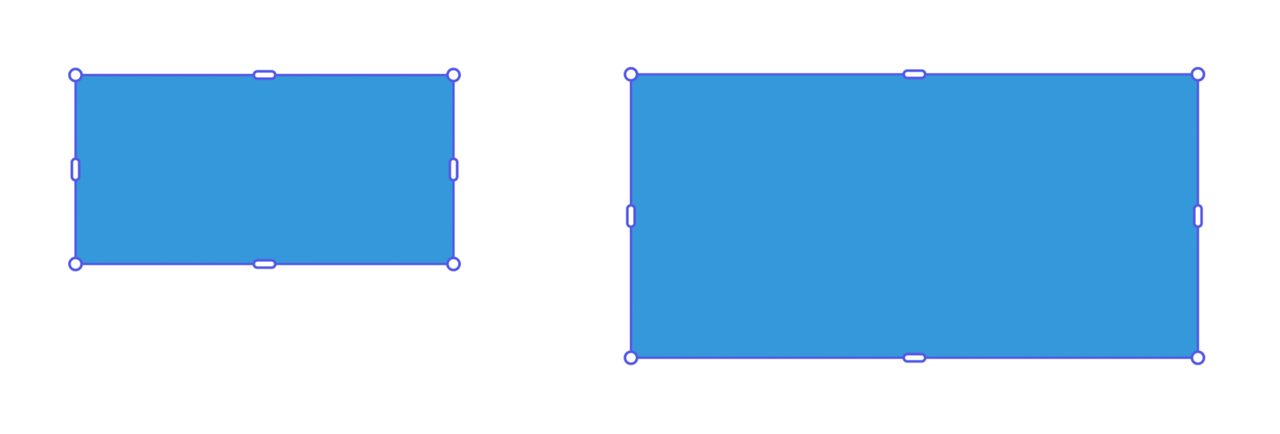
Use rescaleProportionalToWidth() to adjust an element's width while maintaining its aspect ratio. The height will automatically adjust proportionally.
Copied to your clipboard// sandbox/code.jsimport { editor, colorUtils } from "express-document-sdk";// Create a rectangle with specific dimensionsconst rect = editor.createRectangle();rect.width = 200;rect.height = 100;rect.translation = { x: 100, y: 100 };rect.fill = editor.makeColorFill(colorUtils.fromHex("#3498db"));// Add it to the pageeditor.context.insertionParent.children.append(rect);// Rescale to 300px width - height becomes 150px automaticallyrect.rescaleProportionalToWidth(300);console.log(`New dimensions: ${rect.width} x ${rect.height}`);// New dimensions: 300 x 150
Example: Rescale by Height
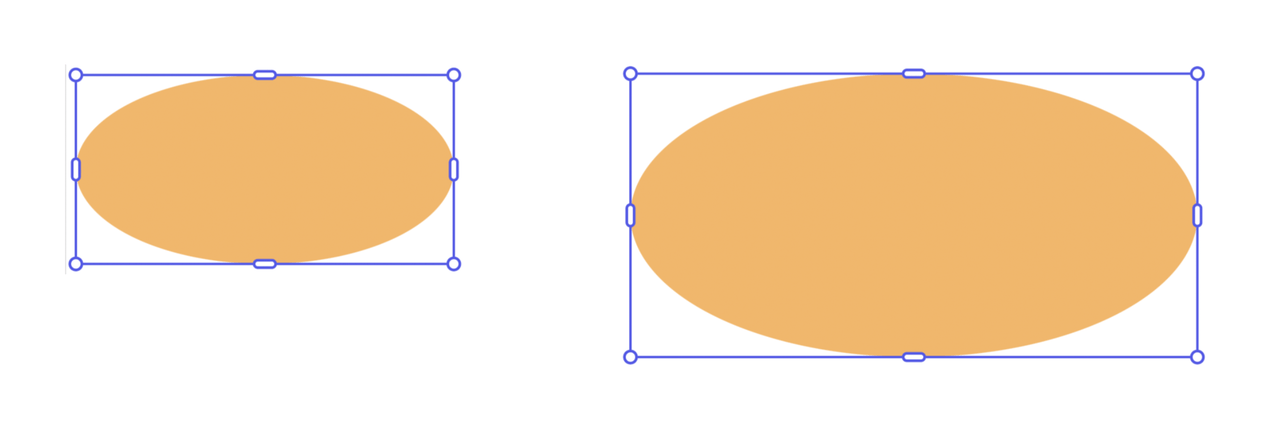
Similarly, use rescaleProportionalToHeight() to adjust an element's height while maintaining its aspect ratio. The width will automatically adjust proportionally.
Copied to your clipboard// sandbox/code.jsimport { editor, colorUtils } from "express-document-sdk";const ellipse = editor.createEllipse();ellipse.rx = 100; // radius x = 100 (width = 200)ellipse.ry = 50; // radius y = 50 (height = 100)ellipse.translation = { x: 150, y: 100 };ellipse.fill = editor.makeColorFill(colorUtils.fromHex("#F0B76C"));editor.context.insertionParent.children.append(ellipse);// Rescale to 150px height - width becomes 300px automaticallyellipse.rescaleProportionalToHeight(150);console.log(`New bounds: ${ellipse.boundsLocal.width} x ${ellipse.boundsLocal.height}`);// New bounds: 300 x 150
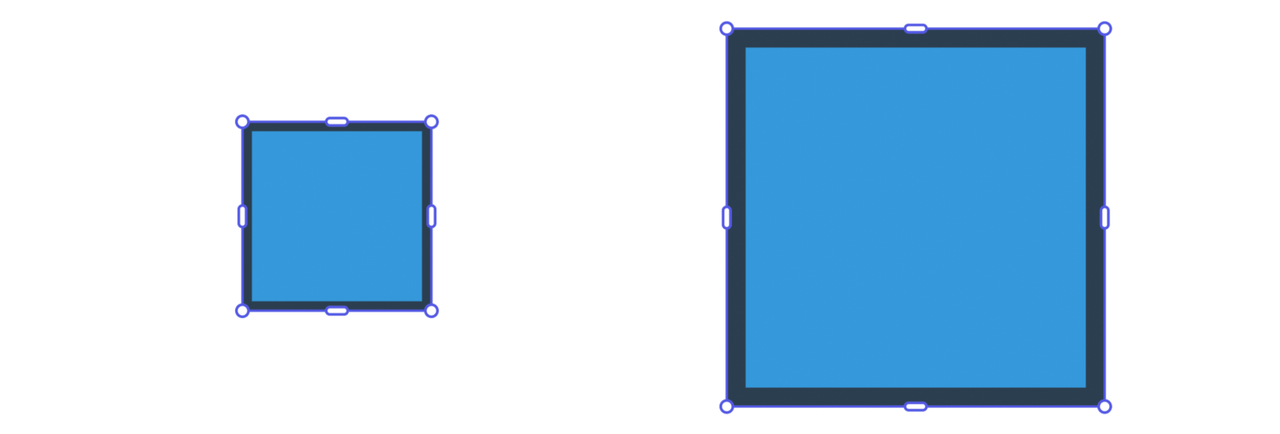
Example: Rescaling with Styled Elements
When rescaling elements with strokes and fills, all visual properties adjust proportionally:
Copied to your clipboard// sandbox/code.js// import { editor, colorUtils, constants } from "express-document-sdk";const rect = editor.createRectangle();rect.width = 100;rect.height = 100;// Apply stylingrect.fill = editor.makeColorFill(colorUtils.fromHex("#3498db"));const stroke = editor.makeStroke({color: colorUtils.fromHex("#2c3e50"),width: 5,position: constants.StrokePosition.inside,});rect.stroke = stroke;editor.context.insertionParent.children.append(rect);// Rescale proportionally - stroke width scales from 5px to 10pxrect.rescaleProportionalToWidth(200);
Resize Elements to Fit Constraints
Resizing operations focus on fitting elements within specific dimensional constraints while trying to preserve visual styling elements at their original sizes.
Example: Resize to Fit Within Bounds (Shapes)
Use resizeToFitWithin() to ensure an element fits entirely within specified dimensions. Elements with fixed aspect ratios may leave unused space on one axis.
Copied to your clipboard// sandbox/code.jsimport { editor } from "express-document-sdk";const rect = editor.createRectangle();rect.width = 300;rect.height = 200;editor.context.insertionParent.children.append(rect);// Resize to fit within a 150x150 boxrect.resizeToFitWithin(150, 150);console.log(`Resized dimensions: ${rect.width} x ${rect.height}`);// Resized dimensions: 150 x 100
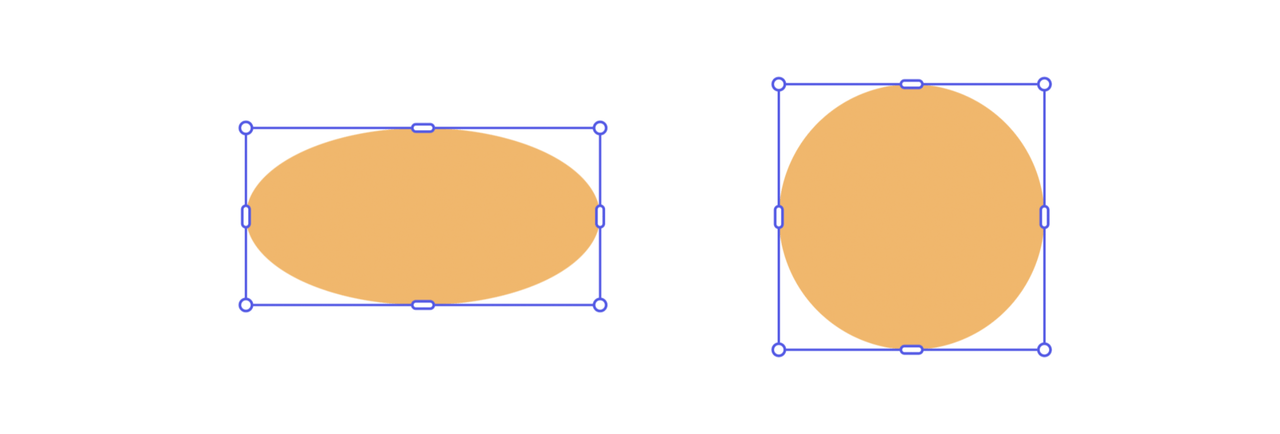
Please note that shapes are resized to fit within a bounding box disregarding their aspect ratio; they are free to extend or shrink on both axes.
Example: Resize to Fit Within Bounds (Media)
Media elements, such as images and videos follow the same rules as shapes.
Copied to your clipboard// sandbox/code.jsimport { editor } from "express-document-sdk";// Assuming the user has selected an Image nodeconst imageNode = editor.context.selection[0];console.log("Initial dimensions: " +imageNode.boundsLocal.width +" x " +imageNode.boundsLocal.height);// Initial dimensions: 300 x 200// Resize to fit within a 150x150 boximageNode.resizeToFitWithin(150, 150);console.log("Resized dimensions: " +imageNode.boundsLocal.width +" x " +imageNode.boundsLocal.height);// Resized dimensions: 150 x 150
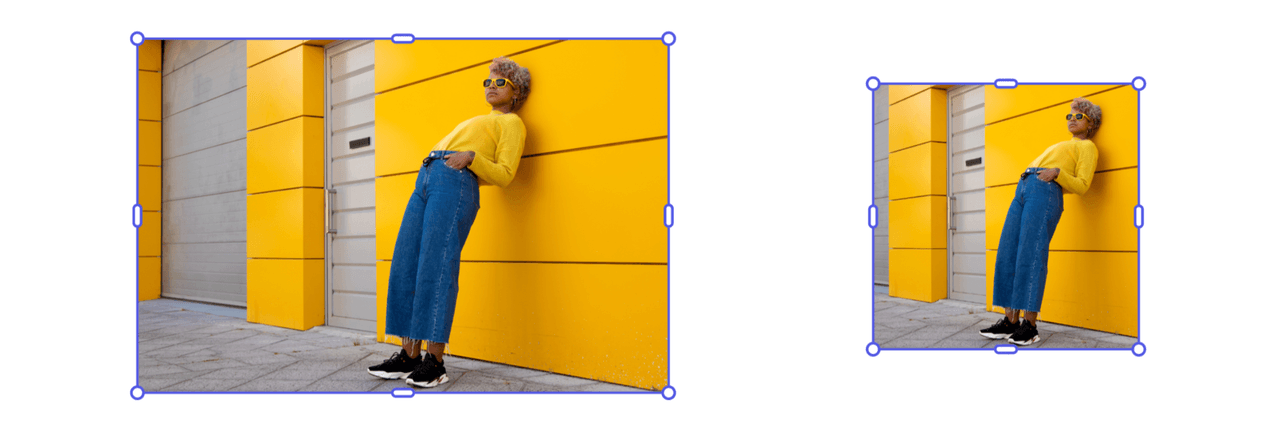

Note that the resize behavior for media elements can differ significantly from shapes, especially when cropping is involved.
This is because the container is resized to fit within the bounding box, while the media inside the container also needs to be adjusted to avoid blank space between the two.
For instance, in the next example we’ll start with the 150x150 image we resized earlier, trying to fit it within a 300x150 box. The results can be counterintuitive, since resize, under the hood, uses a combination of steps to achieve the final dimensions — but it lacks the contextual understanding that Adobe Express has when users interact with the UI. This means that API-based resize calls should always be validated afterward to ensure they produce the expected outcome.
Copied to your clipboard// sandbox/code.jsimport { editor } from "express-document-sdk";// Assuming the user has selected an Image nodeconst imageNode = editor.context.selection[0];console.log("Initial dimensions: " +imageNode.boundsLocal.width +" x " +imageNode.boundsLocal.height);// Initial dimensions: 150 x 150// Resize to fit within a 300x150 boximageNode.resizeToFitWithin(300, 150);console.log("Resized dimensions: " +imageNode.boundsLocal.width +" x " +imageNode.boundsLocal.height);// Resized dimensions: 300 x 150
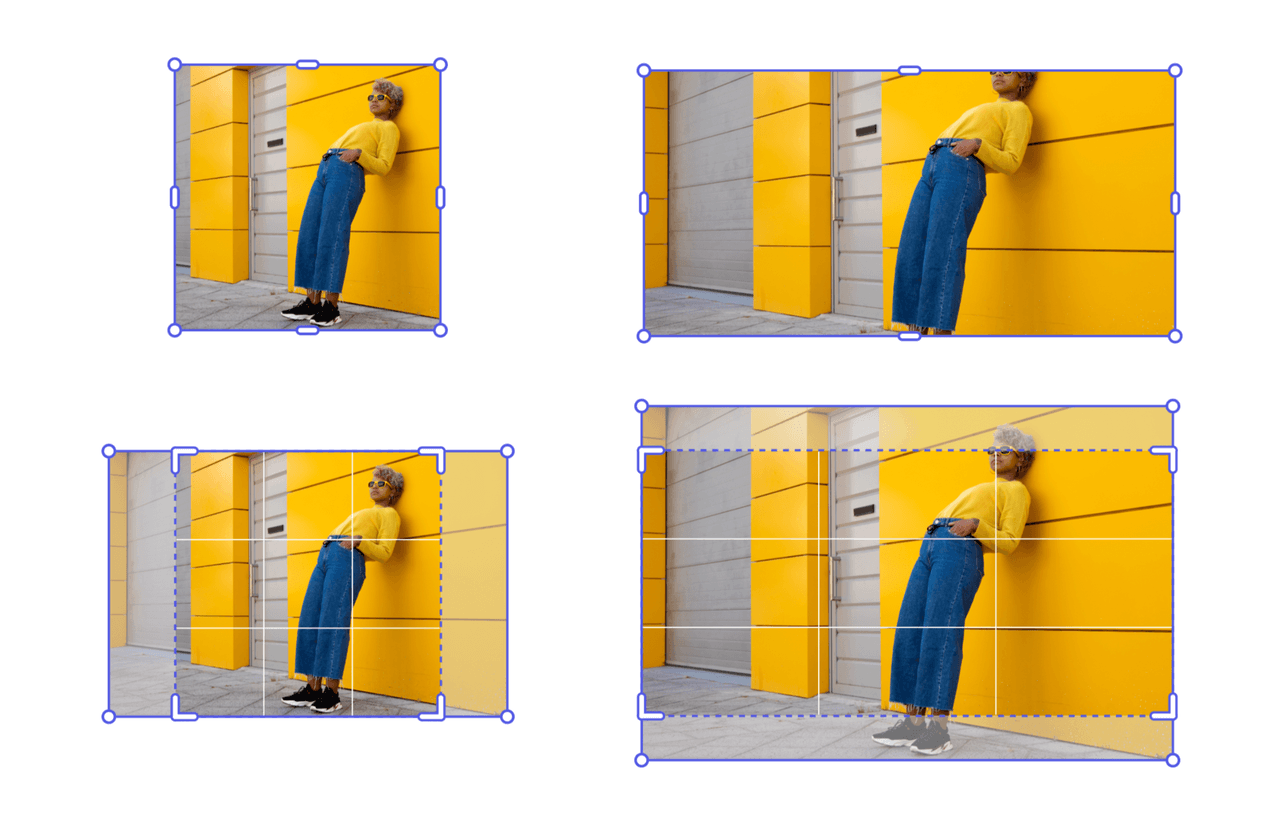
Example: Resize to Cover Area
Use resizeToCover() to ensure an element completely covers the specified dimensions. Elements with fixed aspect ratios may extend outside the target bounds on one axis.
Copied to your clipboard// sandbox/code.jsimport { editor } from "express-document-sdk";// Assuming the user has selected an Image nodeconst imageNode = editor.context.selection[0];console.log("Initial dimensions: " +imageNode.boundsLocal.width +" x " +imageNode.boundsLocal.height);// Initial dimensions: 150 x 100// Resize to cover a 120x120 areaimageNode.resizeToCover(120, 120);console.log("Covered dimensions: " +imageNode.boundsLocal.width +" x " +imageNode.boundsLocal.height);// Covered dimensions: 120 x 120
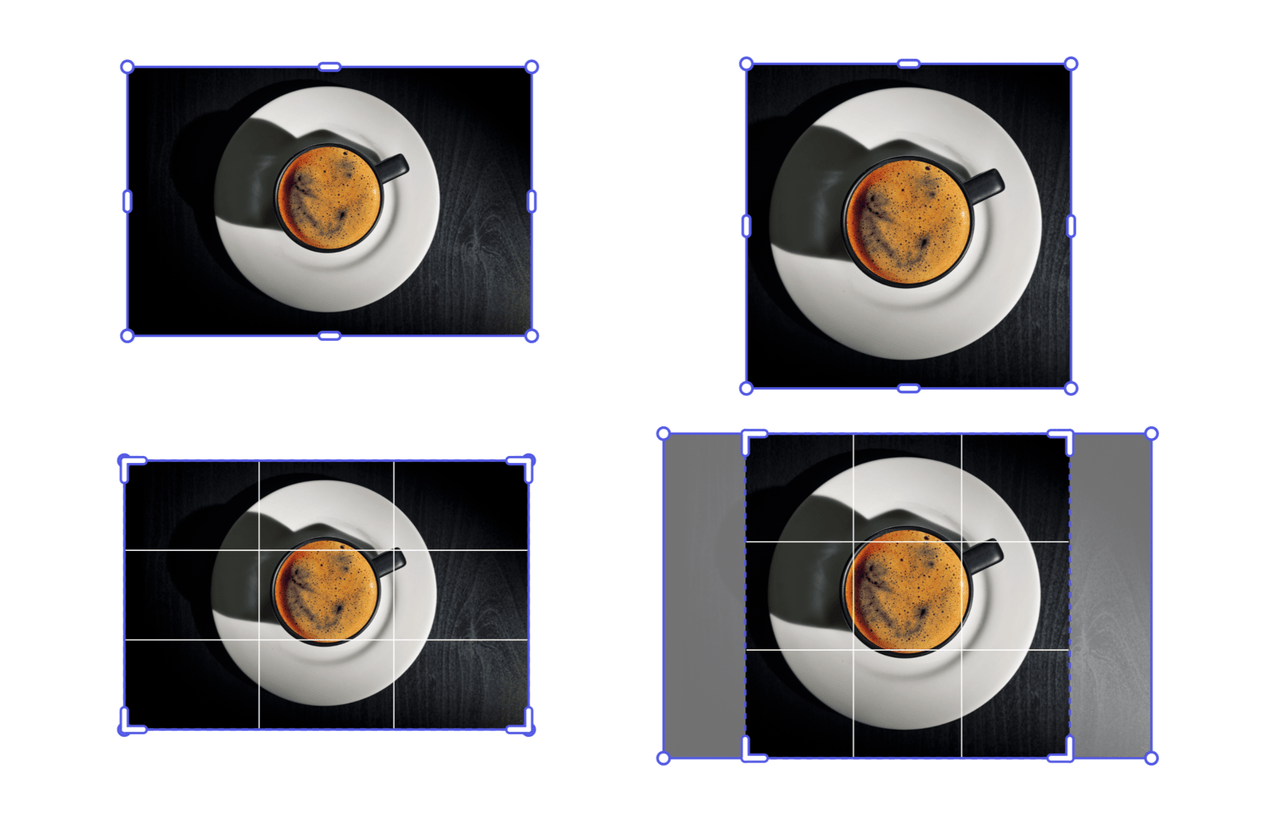
In this example, the image is resized to cover a 120x120 area; the image is enlarged maintaining its aspect ratio, while the crop is adjusted to fit within the bounding box.
With nodes that can resize irrespective of their aspect ratio, like shapes, the resizeToCover() and resizeToFitWithin() methods yield the same result.
Working with Text Elements
Text elements require special considerations when resizing and rescaling, as font sizes and text flow can be affected differently.
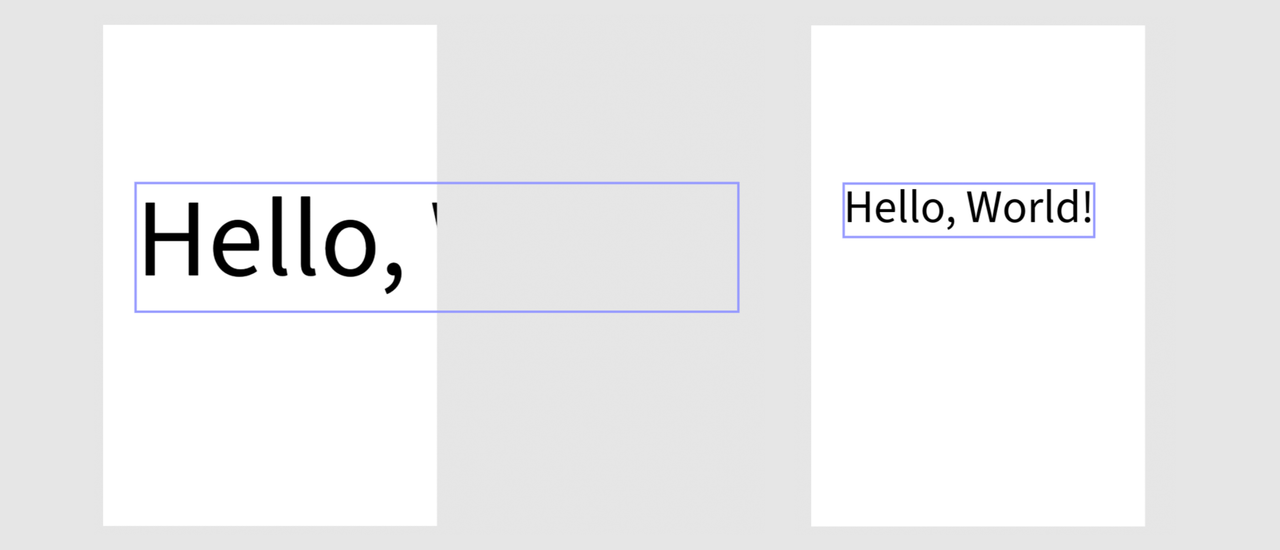
Example: Rescaling Text Proportionally
Copied to your clipboard// sandbox/code.jsimport { editor } from "express-document-sdk";const textNode = editor.createText("Hello, World!");// Center the textconst insertionParent = editor.context.insertionParent;textNode.setPositionInParent({ x: insertionParent.width, y: insertionParent.height / 2 },{ x: 0, y: 0 });insertionParent.children.append(textNode);// Rescale the text proportionally: the font size scales accordingly!textNode.rescaleProportionalToWidth(300);
Example: Similarities between Resizing and Rescaling Text
As we’ve seen, when rescaling text, the font size is adjusted to fit within the specified bounds. The same applies when resizing, which means the four available methods produce pairs of equivalent results then the parameters are set appropriately.
Copied to your clipboard// sandbox/code.js// import { editor } from "express-document-sdk";// Assuming the user has selected a text frameconst textNode = editor.context.selection[0];// Both will result in a 200px wide texttextNode.resizeToFitWithin(200, 100);textNode.rescaleProportionalToWidth(200);// Both will result in a 100px tall texttextNode.resizeToCover(200, 100);textNode.rescaleProportionalToHeight(100);
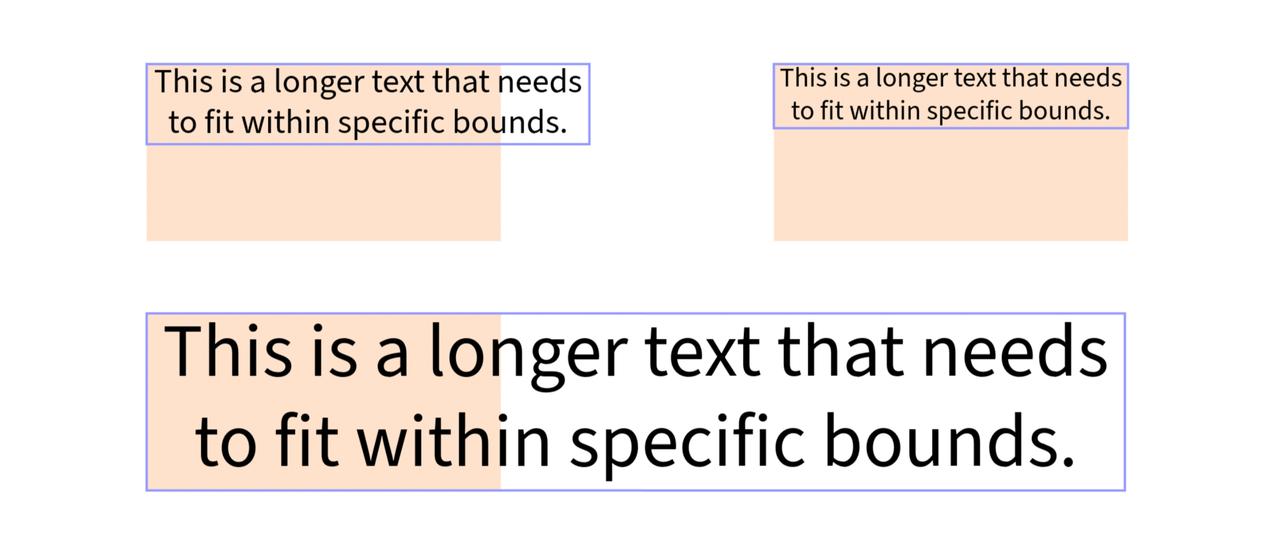
In the screenshot above, the original text is top-left; top-right, the result of both resizeToFitWithin() and rescaleProportionalToWidth(); bottom, resizeToCover()
rescaleProportionalToHeight().
Working with Page Elements
Adjusting the page size is a simpler case of resizing and rescaling. Pages are resized by changing the width and height properties of the PageNode.
Example: Resizing a Page
Copied to your clipboard// sandbox/code.jsimport { editor } from "express-document-sdk";const doc = editor.documentRoot.pages.first;console.log(`Doc's dimensions before: ${doc.width}x${doc.height}`);doc.width = 300;doc.height = 300;console.log(`Doc's dimensions after: ${doc.width}x${doc.height}`);// Doc's dimensions before: 400x600// Doc's dimensions after: 300x300
FAQs
Q: What's the difference between resize and rescale?
A: Resize adjusts bounding box preserving stroke/font sizes; rescale proportionally changes all visual elements.
Q: How do I rescale proportionally by width?
A: Call element.rescaleProportionalToWidth(newWidth) to maintain aspect ratio.
Q: How do I resize to fit within bounds?
A: Call element.resizeToFitWithin(width, height) to fit within specified dimensions.
Q: How do I resize to cover an area?
A: Call element.resizeToCover(width, height) to completely cover the specified area.
Q: Do shapes and media resize differently?
A: Yes, shapes can resize freely; media maintains aspect ratio and may involve cropping.
Q: How does text resizing work?
A: Text resize and rescale methods produce similar results by adjusting font size proportionally.
Q: How do I resize pages?
A: Set page.width and page.height properties directly on the PageNode.

