Using Geometry
Creating Shapes
Adobe Express provides a set of geometric shapes that you can create and style programmatically. These shapes are instances of the RectangleNode and EllipseNode classes, and you can draw them using the editor.createRectangle() and editor.createEllipse() methods, respectively.
Example: Adding a Rectangle
Copied to your clipboard// sandbox/code.jsimport { editor } from "express-document-sdk";const rect = editor.createRectangle();// Define rectangle dimensions.rect.width = 100;rect.height = 100;// The current page, where the rectangle will be placedconst currentPage = editor.context.currentPage;// Append the rectangle to the page.currentPage.artboards.first.children.append(rect);
Creating vs. Adding to the page
Factory methods such as createRectangle() and createEllipse() don't automatically add the shape to the page; while is exists and you can manipulate its properties, it won't be visible until you append it to a container like an Artboard, a Group, or any other instance of a class that implements the ContainerNode interface.
You usually reference the container using editor.context, which provides access to the current page, selection, and other useful properties.
Please note that you can append multiple shapes at once with the append() method:
Copied to your clipboardconst s1 = editor.createRectangle();const s2 = editor.createEllipse();// ... set all properties ...editor.context.currentPage.artboards.first.children.append(s1, s2); // 👈
Example: Adding an Ellipse
Ellipses don't have a width and height properties, but a rx and ry (radius x, radius y) instead.
An ellipse with a radius of 200 on the x-axis and 100 on the y-axis will result in a shape with 400 wide (rx times two) and a 200 tall (ry times two)!
Copied to your clipboard// sandbox/code.jsimport { editor } from "express-document-sdk";const ellipse = editor.createEllipse();ellipse.rx = 200; // radius x 👈ellipse.ry = 100; // radius y 👈console.log(ellipse.boundsLocal);// { x: 0, y: 0, width: 400, height: 200 } 👈 mind the actual bounds!// The current page, where the rectangle will be placedconst currentPage = editor.context.currentPage;// Append the rectangle to the page.currentPage.artboards.first.children.append(rect);
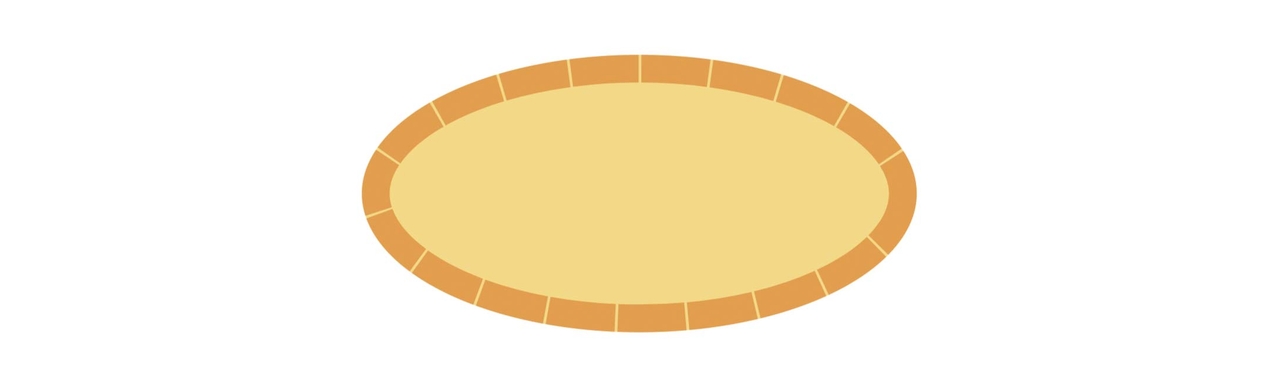
Example: Styling Shapes
Shapes have fill and stroke properties that you can use to style them. The following example demonstrates how to create a rectangle with a fill and a stroke.
Copied to your clipboard// sandbox/code.jsimport { editor, colorUtils, constants } from "express-document-sdk";// Create the shapeconst ellipse = editor.createEllipse();ellipse.rx = 200;ellipse.ry = 100;// 👇 Apply the fill colorellipse.fill = editor.makeColorFill(colorUtils.fromHex("#F3D988"));// 👇 Create the strokeconst stroke = editor.makeStroke({color: colorUtils.fromHex("#E29E4E"),width: 20,position: constants.StrokePosition.inside,dashPattern: [50, 2],});// 👇 Apply the strokeellipse.stroke = stroke;// Add the shape to the documenteditor.context.insertionParent.children.append(ellipse);
If you need a refresher on how to create and apply colors, check out Using Colors.
Creating Paths
Paths are a versatile tool to create complex shapes in Adobe Express. The editor.createPath() method returns an instance of the PathNode class, and accepts one SVG string as the input.
Example: Single path
Copied to your clipboard// sandbox/code.jsimport { editor } from "express-document-sdk";const p1 = editor.createPath(`M224,151L142,151C142,151 145.69,129.772 144,119C147.578,121.515 153.324,124.558 153,124C153.551,119.627 149,115 149,115C154.041,111.701 155.245,104.477 150,110C151.775,105.754 151.55,100.222 146,107C140.45,113.778 150.733,97.726 152,89C153.267,80.274 143.163,79.42 137,77C130.837,74.58 133.264,72.337 133,71C130.052,80.34 126.261,82.078 123,81C119.567,79.866 119.164,65.513 125,57C120.007,59.519 119,58 119,58C128.157,53.412 134.031,44.13 132,42C129.969,39.87 114.451,41.06 106,54C97.549,66.94 99.126,73.868 104,79C96.435,82.127 72,99 72,99C72,99 65.521,102.836 59,102C59.031,109.474 62.37,105.88 65,105C61.399,110.264 61.382,114.8 62,119C64.225,116.9 64,115 64,115C64,115 64.124,118.136 64,122C65.53,120.78 66,119 66,119C66,119 65.324,128.405 66.474,127.387C69.247,124.933 72.234,118.577 74,105C78.171,103.746 106,92 106,92C109.996,104.248 115.941,119.738 112,151L91,151`);editor.context.insertionParent.children.append(p1);
Example: Multiple paths
Combining and grouping multiple paths, you can create complex shapes, like in the following example:
Copied to your clipboard// sandbox/code.jsimport { editor } from "express-document-sdk";const p1 = editor.createPath(`M310,222 A92,92 0 1,0 126,222 A92,92 0 1,0 310,222 Z`);const p2 = editor.createPath(`M425.096,209.235C425.096,209.235 520.492,413.969 554.392,486.722C556.956,492.226 556.533,498.659 553.270,503.779C550.007,508.900 544.355,512.000 538.283,512.000C453.556,512.000 199.784,512.000 115.057,512.000C108.985,512.000 103.333,508.900 100.070,503.779C96.807,498.659 96.384,492.226 98.948,486.722C133.289,413.023 230.896,203.545 230.896,203.545L278.678,236.000 L331.559,195.000 L383.266,236.000 L425.096,209.235 Z`);const p3 = editor.createPath(`M230.896,203.545L278.041,102.365C286.849,83.461 305.815,71.375 326.670,71.375C347.525,71.375 366.491,83.461 375.299,102.365L425.096,209.235 L383.266,236.000 L331.559,195.000L278.678,236.000 L230.896,203.545 Z`);const p4 = editor.createPath(`M218,106 L218,66`);const p5 = editor.createPath(`M160.074,121.590 L140.074,87.150`);const p6 = editor.createPath(`M117.878,164.193 L83.138,144.193`);const p7 = editor.createPath(`M101.831,222.119 L61.831,222.119`);const p8 = editor.createPath(`M118.076,280.194 L83.336,300.194`);const g = editor.createGroup();g.children.append(p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8);editor.context.insertionParent.children.append(g);
Example: Adding Fills and Strokes
PathNode instances have fill and stroke properties that you can use to style the path, very much like, say, a RectangleNode. In the code snippet below, we're going to add some life to the path from the previous example.
Copied to your clipboard// sandbox/code.jsimport { editor } from "express-document-sdk";const p1 = editor.createPath(/* same as before... */);const p2 = editor.createPath(/* same as before... */);const p3 = editor.createPath(/* same as before... */);const p4 = editor.createPath(/* same as before... */);const p5 = editor.createPath(/* same as before... */);const p6 = editor.createPath(/* same as before... */);const p7 = editor.createPath(/* same as before... */);const p8 = editor.createPath(/* same as before... */);const g = editor.createGroup();g.children.append(p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8);// Create a black stroke to apply to all pathsconst blackStroke = editor.makeStroke({color: colorUtils.fromRGB(0, 0, 0, 1),width: 10,});// Apply the stroke to all paths in the groupfor (const path of g.children) {path.stroke = blackStroke;}// Apply different fills to the pathsp1.fill = editor.makeColorFill(colorUtils.fromHex("#f2af0d"));p2.fill = editor.makeColorFill(colorUtils.fromHex("#33cc7b"));p3.fill = editor.makeColorFill(colorUtils.fromHex("#ffffff"));editor.context.insertionParent.children.append(g);