Webhooks signature verification
Because webhook URLs are publicly accessible, it is important to ensure that the incoming requests are sent by Adobe Commerce and not by a third-party actor. You can enable signature verification to ensure your webhooks are secure.
Enable signature verification
Signature verifications are disabled by default, because you might have other ways for securing your webhooks. Authorization headers and IP whitelisting are common techniques.
To enable signature verification, navigate to Stores > Settings > Configuration > Adobe Services > Webhooks and change the Enabled to Yes. Then click Regenerate key pair to generate a new key pair.
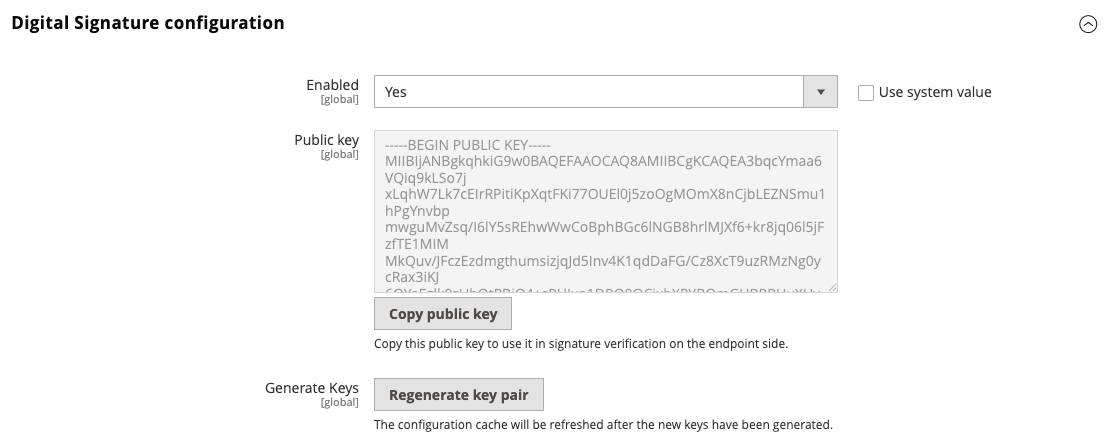
After enabling the signature verification, Commerce adds the x-adobe-commerce-webhook-signature header. The value of this header is a base64 encoded HMAC SHA256 signature of the request body based on the private key.
Verify the signature
To verify the signature you must decode value of x-adobe-commerce-webhook-signature header and compare it with the HMAC SHA256 signature of the base64 encoded request body using the public key from the webhooks configuration.
Here is an example of the verification method of the signature using node.js:
Copied to your clipboardconst fs = require("fs");const crypto = require("crypto");module.exports = {validate: function (req){const publicKey = fs.readFileSync(__dirname + '/publickey', 'utf-8');if (!req.headers['x-adobe-commerce-webhook-signature']) {return false;}const signature = req.headers['x-adobe-commerce-webhook-signature'];const verifier = crypto.createVerify('SHA256');const base64Payload = Buffer.from(JSON.stringify(req.body)).toString('base64');verifier.update(base64Payload);return verifier.verify(publicKey, signature, 'base64');}}
The following example shows how to use the signature verification in the webhook action:
Copied to your clipboardconst signatureValidator = require('../signatureValidator');app.post('/validate-signature', function (req, res) {console.log(JSON.stringify(req.body, null, 4));console.log(JSON.stringify(req.headers, null, 4));let operations = [];if (signatureValidator.validate(req)) {// Perform the webhook actionconsole.log("The signature is valid.");operations.push({op: 'success'});} else {console.log("The signature is invalid.");operations.push({op: 'exception',});}console.log(operations);res.json(operations);});
Keep in mind that when the key pair is regenerated, the old public key will be invalid. You must subsequently update the public key in the signature verification code.
Verify the signature in the App Builder action
To verify the signature in the App Builder action, set the raw-http annotation in the app.config.yaml file. When the raw-http annotation is configured, the HTTP request query and body parameters are passed to the action as reserved properties.
Copied to your clipboardinputs:PUBLIC_KEY: $PUBLIC_KEYannotations:raw-http: true
Store the public key in the PUBLIC_KEY parameter in the .env file using the same format as provided in the Adobe Commerce Admin:
Copied to your clipboard# Other secrets and configuration# ...............................PUBLIC_KEY="-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEAtglXYVz5pVn3HDluGG5Tt9coO5NKSWjx3xCDMHVa3CEqVM76PKg8UJH9fQOA57xoNv7Llc916pF0UswtudQhFyg+WQCFFadqGZOyL2nUKI9xWBiUi4dN8+9yMd3TE1fszVUBnk/XdLKNDQn4O6icdoQZi5arrjNjInkimtcT2jPXs34p9G9P5CvCubPUmbGsWDgwo5an9LEX/nJfnCdZR10XPkRWzEM7o1OGzf7CYo06Xl+msGVM02Er265PsMAWB11cWwKmyg6dLPa8q+QhKNXZiEMvdVusV8aA6EkCZYFdWSBXv+jltn6NnY5qvYcuQ3SujQ9xKEANjeMWcW90PwIDAQAB-----END PUBLIC KEY-----"
Note: Do not commit the .env file to version control.
App Builder Configuration Files describes .env file usage in detail.
The following code example below shows how the signature can be verified in the App Builder action:
Copied to your clipboardconst { Core } = require('@adobe/aio-sdk')const { errorResponse } = require('../utils')const crypto = require('crypto');async function main (params) {const logger = Core.Logger('main', { level: params.LOG_LEVEL || 'info' })try {const signature = params.__ow_headers['x-adobe-commerce-webhook-signature'] || '';const verifier = crypto.createVerify('SHA256');verifier.update(params.__ow_body);const isSignatureValid = verifier.verify(params.PUBLIC_KEY, signature, 'base64');let operations = [];if (isSignatureValid) {logger.info('The signature is valid.');// Here will be performed real action logic// payload is base64 encoded, so we need to decode it before usingconst payload = JSON.parse(atob(params.__ow_body))// a simple validation if the provided postcode from Commerce webhook is less than 50000if (payload.address.postcode > 50000) {operations.push({op: 'exception',message: 'The postcode is not allowed. Provided postcode: ' + payload.address.postcode});} else {operations.push({op: 'success'});}} else {logger.info('The signature is invalid.');operations.push({op: 'exception',message: 'The signature is invalid.'});}return {statusCode: 200,body: JSON.stringify(operations)}} catch (error) {logger.error(error)return errorResponse(500, 'server error', logger)}}exports.main = main

